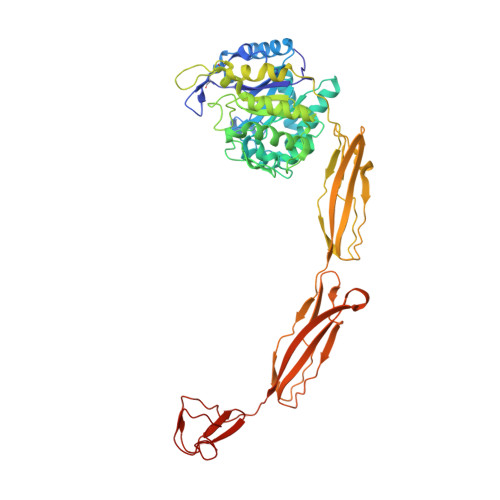
Structure of a complete four-domain chitinase from Moritella marina, a marine psychrophilic bacterium
Malecki, P.H., Raczynska, J.E., Vorgias, C.E., Rypniewski, W.(2013) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 69: 821-829
- PubMed: 23633591
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444913002011
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4HMC, 4HMD, 4HME - PubMed Abstract:
X-ray crystallography reveals chitinase from the psychrophilic bacterium Moritella marina to be an elongated molecule which in addition to the catalytic β/α-barrel domain contains two Ig-like domains and a chitin-binding domain, all linked in a chain. A ligand-binding study using NAG oligomers showed the enzyme to be active in the crystal lattice and resulted in complexes of the protein with oxazolinium ion (the reaction intermediate) and with NAG2, a reaction product. The characteristic motif DXDXE, containing three acidic amino-acid residues, which is a signature of type 18 chitinases, is conserved in the enzyme. Further analysis of the unliganded enzyme with the two protein-ligand complexes and a comparison with other known chitinases elucidated the roles of other conserved residues near the active site. Several features have been identified that are probably important for the reaction mechanism, substrate binding and the efficiency of the enzyme at low temperatures. The chitin-binding domain and the tryptophan patch on the catalytic domain provide general affinity for chitin, in addition to the affinity of the binding site; the two Ig-like domains give the protein a long reach over the chitin surface, and the flexible region between the chitin-binding domain and the adjacent Ig-like domain suggests an ability of the enzyme to probe the surface of the substrate, while the open shallow substrate-binding groove allows easy access to the active site.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, Polish Academy of Sciences, Noskowskiego 12/14, 61-704 Poznan, Poland.