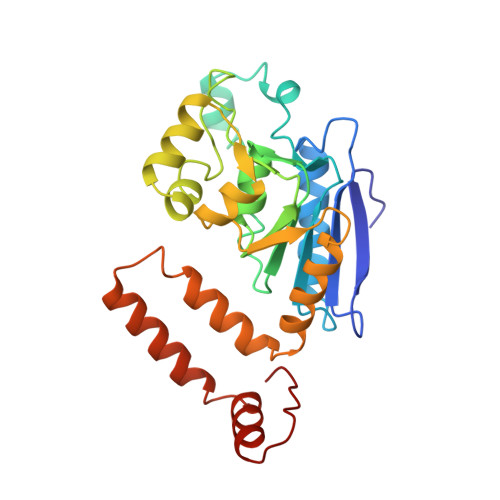
Crystal structure of enoyl-coenzyme A (CoA) hydratase at 2.5 angstroms resolution: a spiral fold defines the CoA-binding pocket.
Engel, C.K., Mathieu, M., Zeelen, J.P., Hiltunen, J.K., Wierenga, R.K.(1996) EMBO J 15: 5135-5145
- PubMed: 8895557
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1DUB - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of rat liver mitochondrial enoyl-coenzyme A (CoA) hydratase complexed with the potent inhibitor acetoacetyl-CoA has been refined at 2.5 angstroms resolution. This enzyme catalyses the reversible addition of water to alpha,beta-unsaturated enoyl-CoA thioesters, with nearly diffusion-controlled reaction rates for the best substrates. Enoyl-CoA hydratase is a hexamer of six identical subunits of 161 kDa molecular mass for the complex. The hexamer is a dimer of trimers. The monomer is folded into a right-handed spiral of four turns, followed by two small domains which are involved in trimerization. Each turn of the spiral consists of two beta-strands and an alpha-helix. The mechanism for the hydratase/dehydratase reaction follows a syn-stereochemistry, a preference that is opposite to the nonenzymatic reaction. The active-site architecture agrees with this stereochemistry. It confirms the importance of Glu164 as the catalytic acid for providing the alpha-proton during the hydratase reaction. It also shows the importance of Glu144 as the catalytic base for the activation of a water molecule in the hydratase reaction. The comparison of an unliganded and a liganded active site within the same crystal form shows a water molecule in the unliganded subunit. This water molecule is bound between the two catalytic glutamates and could serve as the activated water during catalysis.
Organizational Affiliation:
European Molecular Biology Laboratory, Heidelberg, Germany.