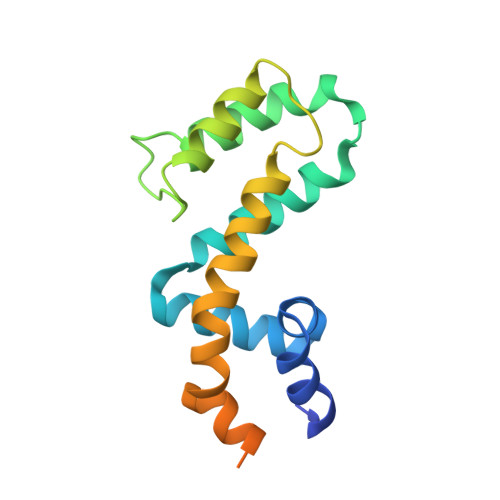
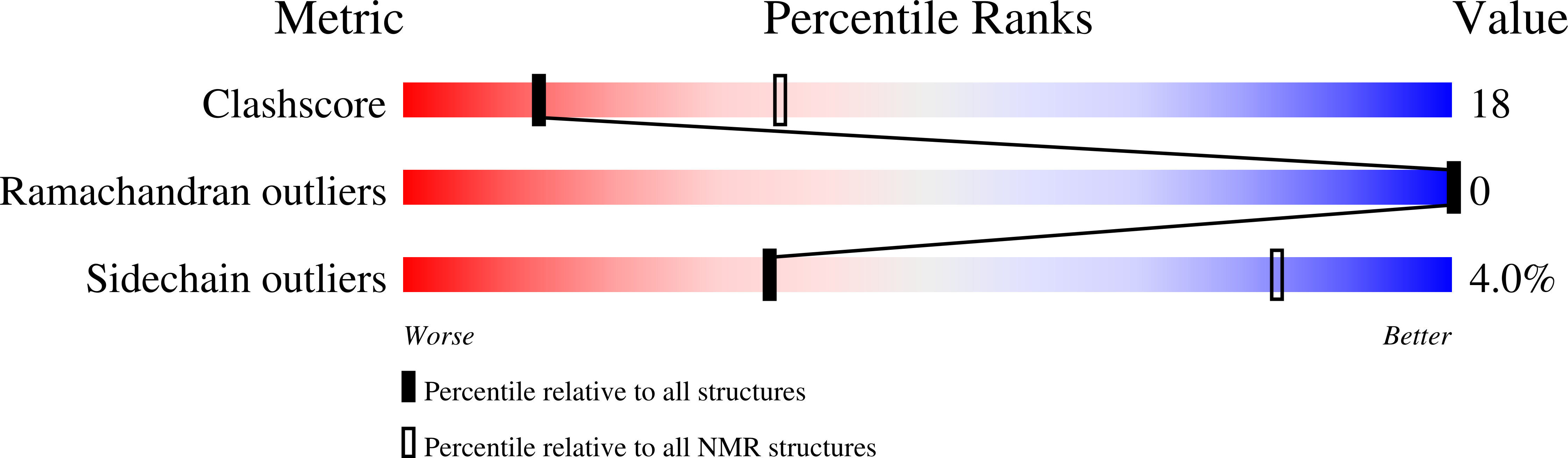NMR structure of free RGS4 reveals an induced conformational change upon binding Galpha.
Moy, F.J., Chanda, P.K., Cockett, M.I., Edris, W., Jones, P.G., Mason, K., Semus, S., Powers, R.(2000) Biochemistry 39: 7063-7073
- PubMed: 10852703
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi992760w
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1EZT, 1EZY - PubMed Abstract:
Heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G-proteins) are transducers in many cellular transmembrane signaling systems where regulators of G-protein signaling (RGS) act as attenuators of the G-protein signal cascade by binding to the Galpha subunit of G-proteins (G(i)(alpha)(1)) and increasing the rate of GTP hydrolysis. The high-resolution solution structure of free RGS4 has been determined using two-dimensional and three-dimensional heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy. A total of 30 structures were calculated by means of hybrid distance geometry-simulated annealing using a total of 2871 experimental NMR restraints. The atomic rms distribution about the mean coordinate positions for residues 5-134 for the 30 structures is 0.47 +/- 0.05 A for the backbone atoms, 0. 86 +/- 0.05 A for all atoms, and 0.56 +/- 0.04 A for all atoms excluding disordered side chains. The NMR solution structure of free RGS4 suggests a significant conformational change upon binding G(i)(alpha)(1) as evident by the backbone atomic rms difference of 1. 94 A between the free and bound forms of RGS4. The underlying cause of this structural change is a perturbation in the secondary structure elements in the vicinity of the G(i)(alpha)(1) binding site. A kink in the helix between residues K116-Y119 is more pronounced in the RGS4-G(i)(alpha)(1) X-ray structure relative to the free RGS4 NMR structure, resulting in a reorganization of the packing of the N-terminal and C-terminal helices. The presence of the helical disruption in the RGS4-G(i)(alpha)(1) X-ray structure allows for the formation of a hydrogen-bonding network within the binding pocket for G(i)(alpha)(1) on RGS4, where RGS4 residues D117, S118, and R121 interact with residue T182 from G(i)(alpha)(1). The binding pocket for G(i)(alpha)(1) on RGS4 is larger and more accessible in the free RGS4 NMR structure and does not present the preformed binding site observed in the RGS4-G(i)(alpha)(1) X-ray structure. This observation implies that the successful complex formation between RGS4 and G(i)(alpha)(1) is dependent on both the formation of the bound RGS4 conformation and the proper orientation of T182 from G(i)(alpha)(1). The observed changes for the free RGS4 NMR structure suggest a mechanism for its selectivity for the Galpha-GTP-Mg(2+) complex and a means to facilitate the GTPase cycle.
Organizational Affiliation:
Departments of Biological Chemistry and Neurosciences, Wyeth Research, Cambridge, MA 02140, USA.