RNA Synthesis in a Cage--Structural Studies of Reovirus Polymerase [lambda] 3
Tao, Y., Farsetta, D.L., Nibert, M.L., Harrison, S.C.(2002) Cell 111: 733-745
- PubMed: 12464184
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(02)01110-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1MUK, 1MWH, 1N1H, 1N35, 1N38 - PubMed Abstract:
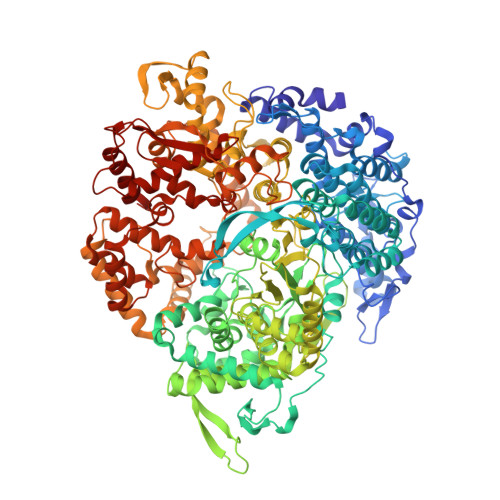
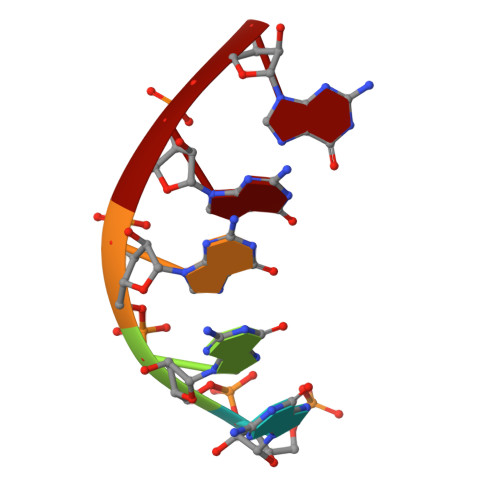
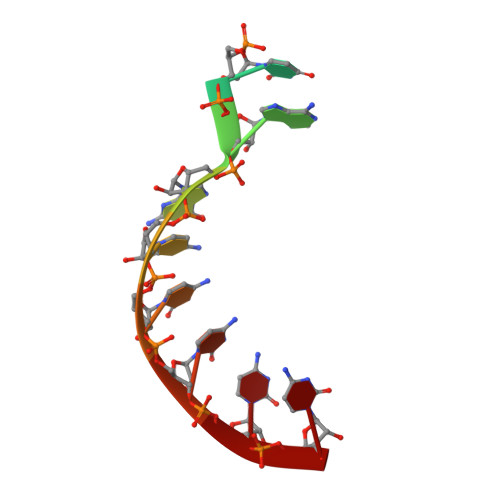
The reovirus polymerase and those of other dsRNA viruses function within the confines of a protein capsid to transcribe the tightly packed dsRNA genome segments. The crystal structure of the reovirus polymerase, lambda3, determined at 2.5 A resolution, shows a fingers-palm-thumb core, similar to those of other viral polymerases, surrounded by major N- and C-terminal elaborations, which create a cage-like structure, with four channels leading to the catalytic site. This "caged" polymerase has allowed us to visualize the results of several rounds of RNA polymerization directly in the crystals. A 5' cap binding site on the surface of lambda3 suggests a template retention mechanism by which attachment of the 5' end of the plus-sense strand facilitates insertion of the 3' end of the minus-sense strand into the template channel.
Organizational Affiliation:
Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA 02138, USA.