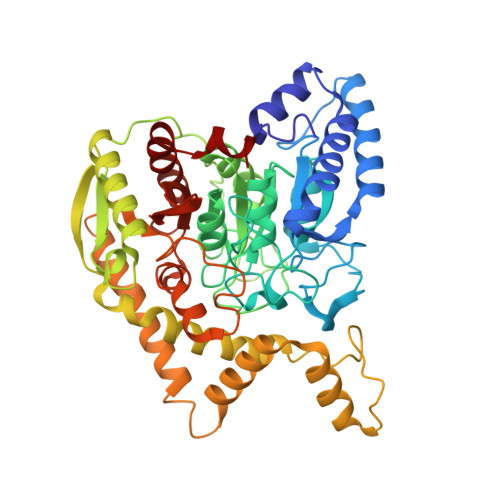
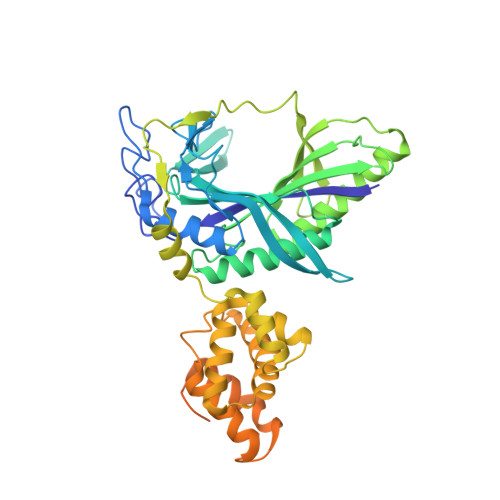
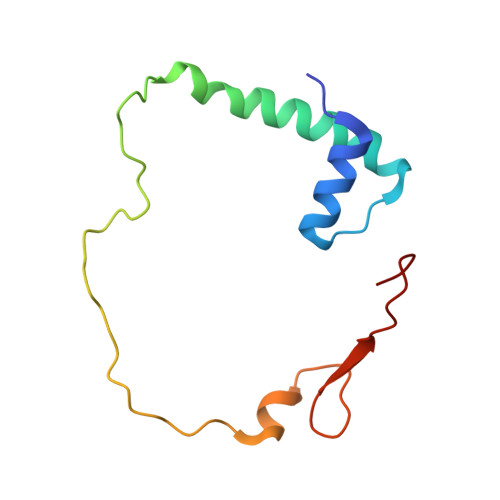
Ammonia channel couples glutaminase with transamidase reactions in GatCAB
Nakamura, A., Yao, M., Chimnaronk, S., Sakai, N., Tanaka, I.(2006) Science 312: 1954-1958
- PubMed: 16809541
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1127156
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2DF4, 2DQN, 2F2A, 2G5H, 2G5I - PubMed Abstract:
The formation of glutaminyl transfer RNA (Gln-tRNA(Gln)) differs among the three domains of life. Most bacteria employ an indirect pathway to produce Gln-tRNA(Gln) by a heterotrimeric glutamine amidotransferase CAB (GatCAB) that acts on the misacylated Glu-tRNA(Gln). Here, we describe a series of crystal structures of intact GatCAB from Staphylococcus aureus in the apo form and in the complexes with glutamine, asparagine, Mn2+, and adenosine triphosphate analog. Two identified catalytic centers for the glutaminase and transamidase reactions are markedly distant but connected by a hydrophilic ammonia channel 30 A in length. Further, we show that the first U-A base pair in the acceptor stem and the D loop of tRNA(Gln) serve as identity elements essential for discrimination by GatCAB and propose a complete model for the overall concerted reactions to synthesize Gln-tRNA(Gln).
Organizational Affiliation:
Faculty of Advanced Life Sciences, Hokkaido University, Sapporo 060-0810, Japan.