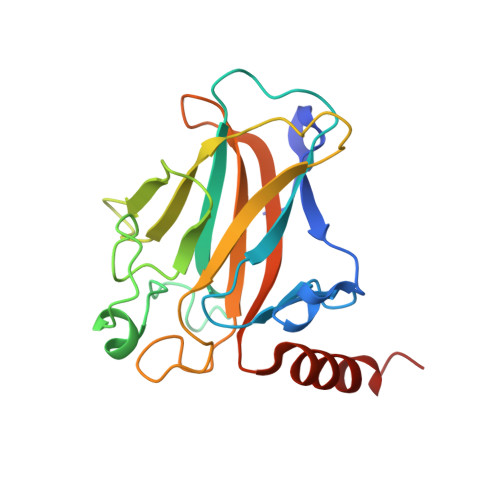
Crystal structure of a p53 core tetramer bound to DNA.
Malecka, K.A., Ho, W.C., Marmorstein, R.(2009) Oncogene 28: 325-333
- PubMed: 18978813
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.400
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3EXJ, 3EXL - PubMed Abstract:
The tumor suppressor p53 regulates downstream genes in response to many cellular stresses and is frequently mutated in human cancers. Here, we report the use of a crosslinking strategy to trap a tetrameric p53 DNA-binding domain (p53DBD) bound to DNA and the X-ray crystal structure of the protein/DNA complex. The structure reveals that two p53DBD dimers bind to B form DNA with no relative twist and that a p53 tetramer can bind to DNA without introducing significant DNA bending. The numerous dimer-dimer interactions involve several strictly conserved residues, thus suggesting a molecular basis for p53DBD-DNA binding cooperativity. Surface residue conservation of the p53DBD tetramer bound to DNA highlights possible regions of other p53 domain or p53 cofactor interactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Wistar Institute, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA.