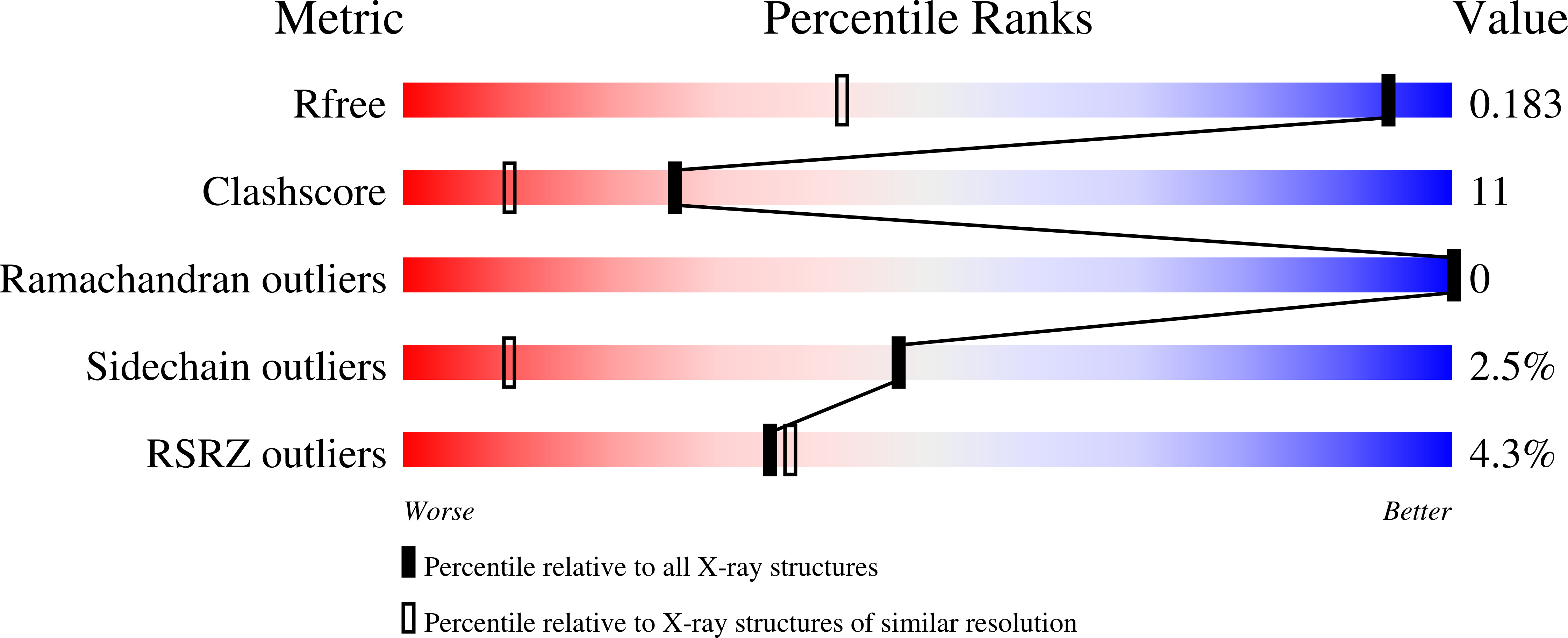
Residue Phe112 of the human-type corrinoid adenosyltransferase (PduO) enzyme of Lactobacillus reuteri is critical to the formation of the four-coordinate Co(II) corrinoid substrate and to the activity of the enzyme.
Mera, P.E., St Maurice, M., Rayment, I., Escalante-Semerena, J.C.(2009) Biochemistry 48: 3138-3145
- PubMed: 19236001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi9000134
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3GAH, 3GAI, 3GAJ - PubMed Abstract:
ATP:Corrinoid adenosyltransferases (ACAs) catalyze the transfer of the adenosyl moiety from ATP to cob(I)alamin via a four-coordinate cob(II)alamin intermediate. At present, it is unknown how ACAs promote the formation of the four-coordinate corrinoid species needed for activity. The published high-resolution crystal structure of the ACA from Lactobacillus reuteri (LrPduO) in complex with ATP and cob(II)alamin shows that the environment around the alpha face of the corrin ring consists of bulky hydrophobic residues. To understand how these residues promote the generation of the four-coordinate cob(II)alamin, variants of the human-type ACA enzyme from L. reuteri (LrPduO) were kinetically and structurally characterized. These studies revealed that residue Phe112 is critical in the displacement of 5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole (DMB) from its coordination bond with the Co ion of the ring, resulting in the formation of the four-coordinate species. An F112A substitution resulted in a 80% drop in the catalytic efficiency of the enzyme. The explanation for this loss of activity was obtained from the crystal structure of the mutant protein, which showed cob(II)alamin bound in the active site with DMB coordinated to the cobalt ion. The crystal structure of an LrPduO(F112H) variant showed a DMB-off/His-on interaction between the corrinoid and the enzyme, whose catalytic efficiency was 4 orders of magnitude lower than that of the wild-type protein. The analysis of the kinetic parameters of LrPduO(F112H) suggests that the F112H substitution negatively impacts product release. Substitutions of other hydrophobic residues in the Cbl binding pocket did not result in significant defects in catalytic efficiency in vitro; however, none of the variant enzymes analyzed in this work supported AdoCbl biosynthesis in vivo.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Bacteriology, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin 53706, USA.