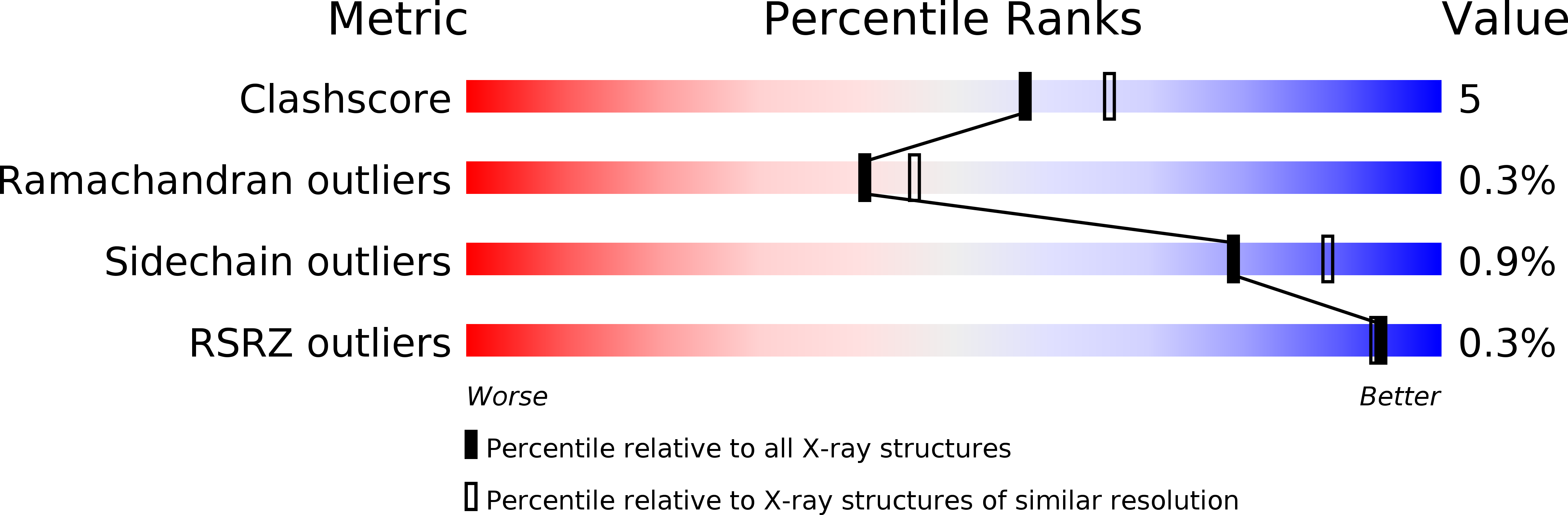
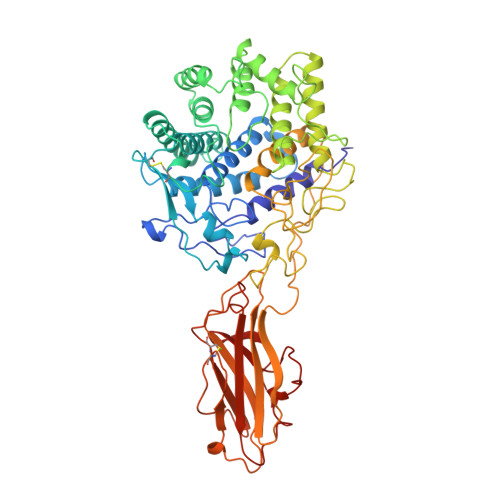
Structure and mechanism of endo/exocellulase E4 from Thermomonospora fusca.
Sakon, J., Irwin, D., Wilson, D.B., Karplus, P.A.(1997) Nat Struct Biol 4: 810-818
- PubMed: 9334746
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb1097-810
- PubMed Abstract:
Cellulase E4 from Thermomonospora fusca is unusual in that it has characteristics of both exo- and endo-cellulases. Here we report the crystal structure of a 68K M(r) fragment of E4 (E4-68) at 1.9 A resolution. E4-68 contains both a family 9 catalytic domain, exhibiting an (alpha/alpha)6 barrel fold, and a family III cellulose binding domain, having an antiparallel beta-sandwich fold. While neither of these folds is novel, E4-68 provides the first cellulase structure having interacting catalytic and cellulose binding domains. The complexes of E4-68 with cellopentaose, cellotriose and cellobiose reveal conformational changes associated with ligand binding and allow us to propose a catalytic mechanism for family 9 enzymes. We also provide evidence that E4 has two novel characteristics: first it combines exo- and endo-activities and second, when it functions as an exo-cellulase, it cleaves off cellotetraose units.
Organizational Affiliation:
Section of Biochemistry, Molecular and Cell Biology, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York 14853, USA.