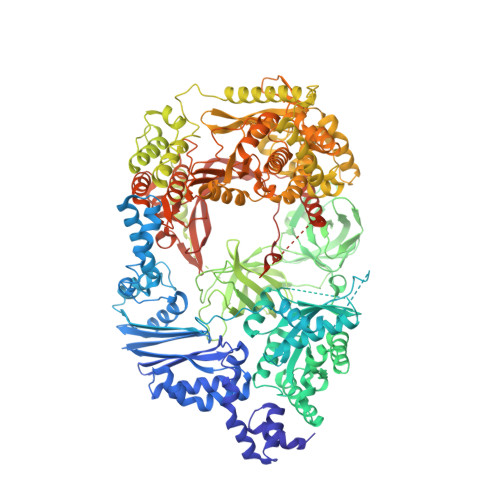
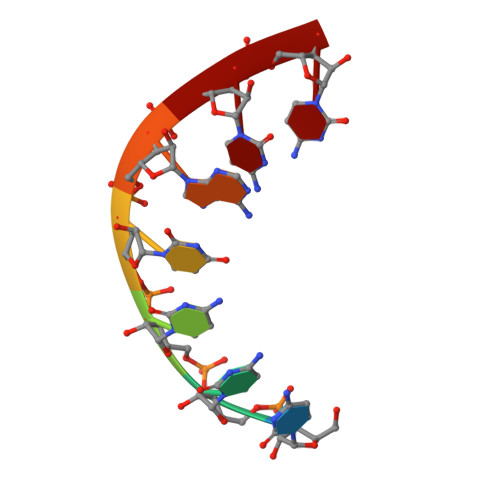
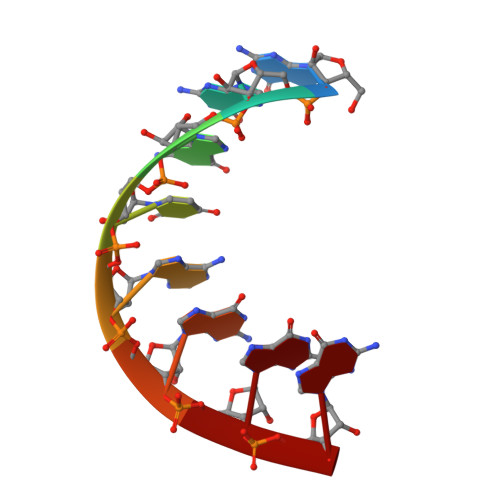
Mechanism for template-independent terminal adenylation activity of Q beta replicase
Takeshita, D., Yamashita, S., Tomita, K.(2012) Structure 20: 1661-1669
- PubMed: 22884418
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2012.07.004
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3VNU, 3VNV, 4FWT - PubMed Abstract:
The genomic RNA of Qβ virus is replicated by Qβ replicase, a template-dependent RNA polymerase complex. Qβ replicase has an intrinsic template-independent RNA 3'-adenylation activity, which is required for efficient viral RNA amplification in the host cells. However, the mechanism of the template-independent 3'-adenylation of RNAs by Qβ replicase has remained elusive. We determined the structure of a complex that includes Qβ replicase, a template RNA, a growing RNA complementary to the template RNA, and ATP. The structure represents the terminal stage of RNA polymerization and reveals that the shape and size of the nucleotide-binding pocket becomes available for ATP accommodation after the 3'-penultimate template-dependent C-addition. The stacking interaction between the ATP and the neighboring Watson-Crick base pair, between the 5'-G in the template and the 3'-C in the growing RNA, contributes to the nucleotide specificity. Thus, the template for the template-independent 3'-adenylation by Qβ replicase is the RNA and protein ribonucleoprotein complex.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biomedical Research Institute, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, 1-1-1, Higashi, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8566, Japan.