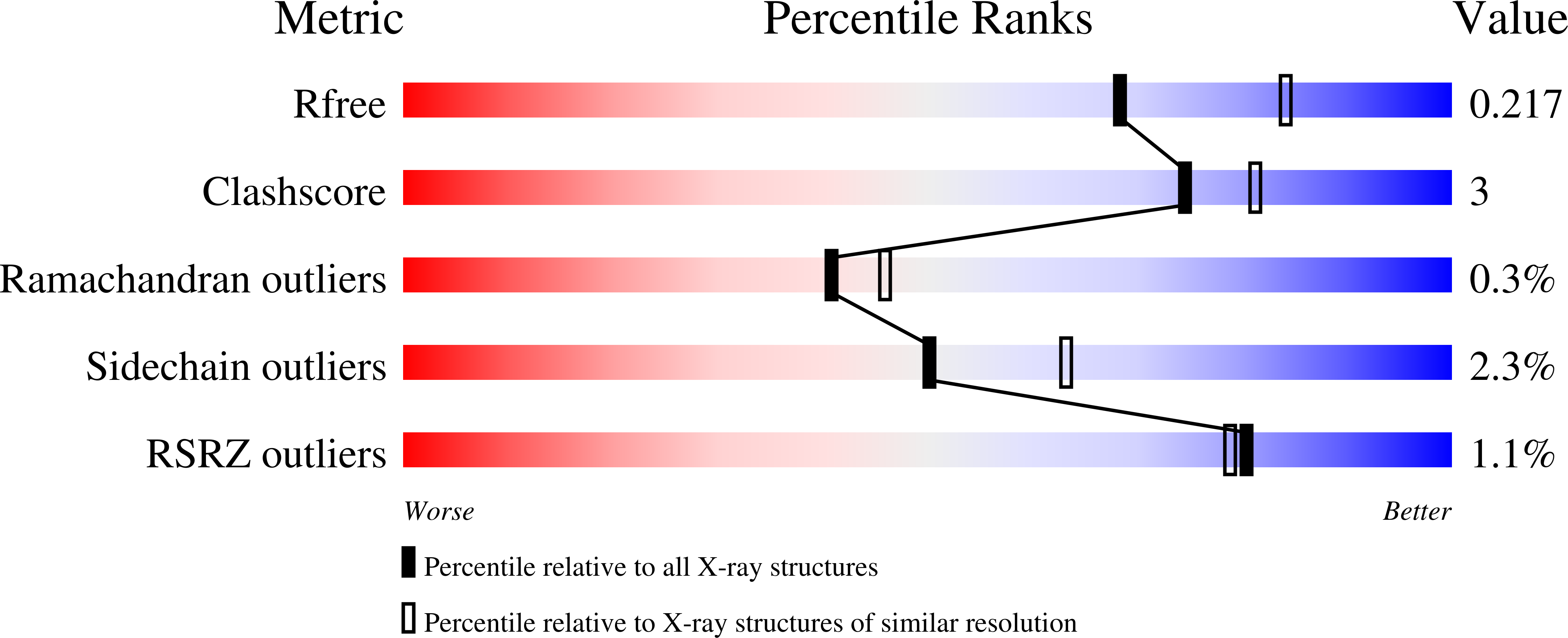
2-Substituted-2-amino-6-boronohexanoic acids as arginase inhibitors.
Golebiowski, A., Paul Beckett, R., Van Zandt, M., Ji, M.K., Whitehouse, D., Ryder, T.R., Jagdmann, E., Andreoli, M., Mazur, A., Padmanilayam, M., Cousido-Siah, A., Mitschler, A., Ruiz, F.X., Podjarny, A., Schroeter, H.(2013) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23: 2027-2030
- PubMed: 23453840
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.02.024
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4IE1, 4IE2, 4IE3 - PubMed Abstract:
Substitution at the alpha center of the known human arginase inhibitor 2-amino-6-boronohexanoic acid (ABH) is acceptable in the active site pockets of both human arginase I and arginase II. In particular, substituents with a tertiary amine linked via a two carbon chain show improved inhibitory potency for both enzyme isoforms. This potency improvement can be rationalized by X-ray crystallography, which shows a water-mediated contact between the basic nitrogen and the carboxylic acid side chain of Asp200, which is situated at the mouth of the active site pocket of arginase II (Asp181 in arginase I). We believe that this is the first literature report of compounds with improved arginase inhibitory activity, relative to ABH, and represents a promising starting point for further optimization of in vitro potency and the identification of better tool molecules for in vivo investigations of the potential pathophysiological roles of arginases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institutes for Pharmaceutical Discovery, 23 Business Park Drive, Branford, CT, USA. [email protected]