Unnatural Cytosine Bases Recognized as Thymines by DNA Polymerases by the Formation of the Watson-Crick Geometry.
Zeng, H., Mondal, M., Song, R., Zhang, J., Xia, B., Liu, M., Zhu, C., He, B., Gao, Y.Q., Yi, C.(2019) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 58: 130-133
- PubMed: 30407705
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201807845
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
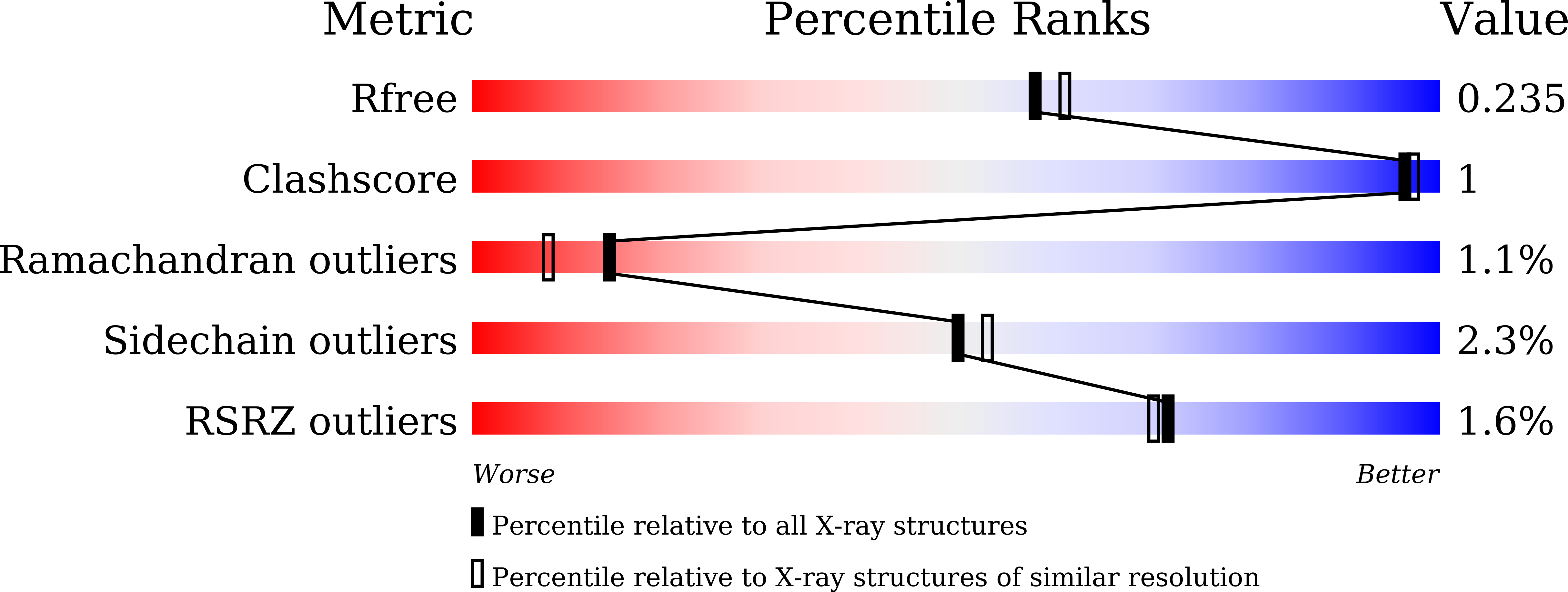
5YTC, 5YTD, 5YTE, 5YTF, 5YTG, 5YTH, 5Z3N - PubMed Abstract:
The emergence of unnatural DNA bases provides opportunities to demystify the mechanisms by which DNA polymerases faithfully decode chemical information on the template. It was previously shown that two unnatural cytosine bases (termed "M-fC" and "I-fC"), which are chemical labeling adducts of the epigenetic base 5-formylcytosine, can induce C-to-T transition during DNA amplification. However, how DNA polymerases recognize such unnatural cytosine bases remains enigmatic. Herein, crystal structures of unnatural cytosine bases pairing to dA/dG in the KlenTaq polymerase-host-guest complex system and pairing to dATP in the KlenTaq polymerase active site were determined. Both M-fC and I-fC base pair with dA/dATP, but not with dG, in a Watson-Crick geometry. This study reveals that the formation of the Watson-Crick geometry, which may be enabled by the A-rule, is important for the recognition of unnatural cytosines.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Life Sciences, Department of Chemical Biology and Synthetic and Functional Biomolecules Center, College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering and Peking-Tsinghua Center for Life Sciences, Peking University, Beijing, 100871, China.