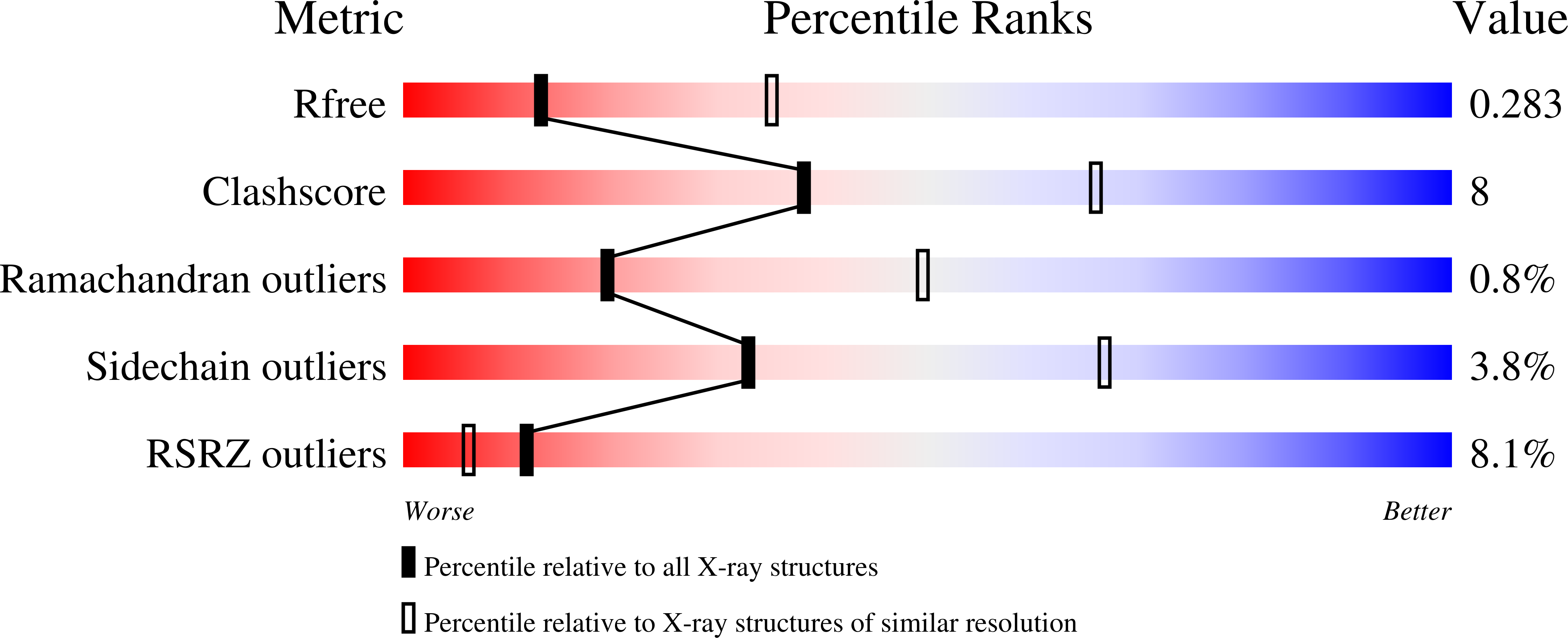
Chlorophyll a/b binding-specificity in water-soluble chlorophyll protein.
Palm, D.M., Agostini, A., Averesch, V., Girr, P., Werwie, M., Takahashi, S., Satoh, H., Jaenicke, E., Paulsen, H.(2018) Nat Plants 4: 920-929
- PubMed: 30297830
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-018-0273-z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6GIW, 6GIX - PubMed Abstract:
We altered the chlorophyll (Chl) binding sites in various versions of water-soluble chlorophyll protein (WSCP) by amino acid exchanges to alter their preferences for either Chl a or Chl b. WSCP is ideally suited for this mutational analysis since it forms a tetrameric complex with only four identical Chl binding sites. A loop of 4-6 amino acids is responsible for Chl a versus Chl b selectivity. We show that a single amino acid exchange within this loop changes the relative Chl a/b affinities by a factor of 40. We obtained crystal structures of this WSCP variant binding either Chl a or Chl b. The Chl binding sites in these structures were compared with those in the major light-harvesting complex (LHCII) of the photosynthetic apparatus in plants to search for similar structural features involved in Chl a/b binding specificity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Molecular Physiology, Johannes Gutenberg-University, Mainz, Germany.