AtFKBP53: a chimeric histone chaperone with functional nucleoplasmin and PPIase domains.
Singh, A.K., Datta, A., Jobichen, C., Luan, S., Vasudevan, D.(2020) Nucleic Acids Res 48: 1531-1550
- PubMed: 31807785
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz1153
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
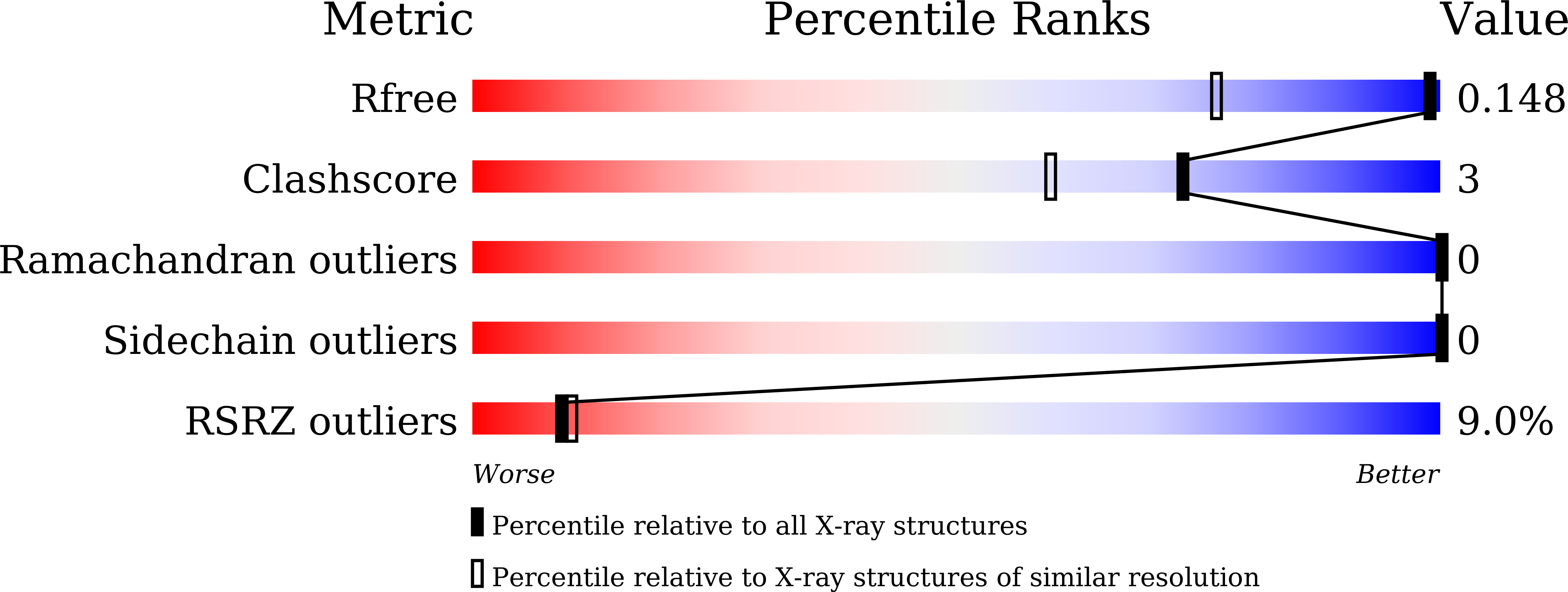
6J2M, 6J2Z - PubMed Abstract:
FKBP53 is one of the seven multi-domain FK506-binding proteins present in Arabidopsis thaliana, and it is known to get targeted to the nucleus. It has a conserved PPIase domain at the C-terminus and a highly charged N-terminal stretch, which has been reported to bind to histone H3 and perform the function of a histone chaperone. To better understand the molecular details of this PPIase with histone chaperoning activity, we have solved the crystal structures of its terminal domains and functionally characterized them. The C-terminal domain showed strong PPIase activity, no role in histone chaperoning and revealed a monomeric five-beta palm-like fold that wrapped over a helix, typical of an FK506-binding domain. The N-terminal domain had a pentameric nucleoplasmin-fold; making this the first report of a plant nucleoplasmin structure. Further characterization revealed the N-terminal nucleoplasmin domain to interact with H2A/H2B and H3/H4 histone oligomers, individually, as well as simultaneously, suggesting two different binding sites for H2A/H2B and H3/H4. The pentameric domain assists nucleosome assembly and forms a discrete complex with pre-formed nucleosomes; wherein two pentamers bind to a nucleosome.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Life Sciences, Nalco Square, Chandrasekharpur, Bhubaneswar 751023, India.