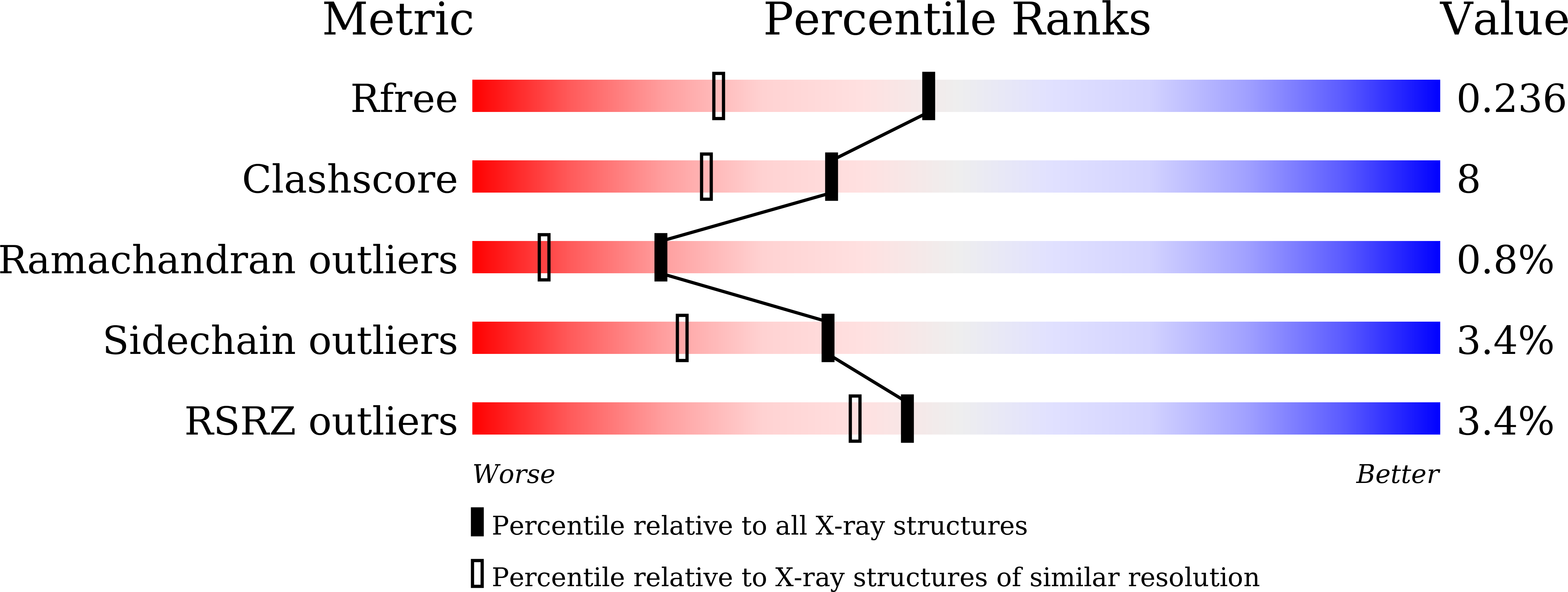
PPAR alpha Ligand-Binding Domain Structures with Endogenous Fatty Acids and Fibrates.
Kamata, S., Oyama, T., Saito, K., Honda, A., Yamamoto, Y., Suda, K., Ishikawa, R., Itoh, T., Watanabe, Y., Shibata, T., Uchida, K., Suematsu, M., Ishii, I.(2020) iScience 23: 101727-101727
- PubMed: 33205029
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2020.101727
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6KAX, 6KAY, 6KAZ, 6KB0, 6KB1, 6KB2, 6KB3, 6KB4, 6KB5, 6KB6, 6KB7, 6KB8, 6KB9, 6KBA, 6KYP, 6L36, 6L37, 6L38, 6LX4, 6LX5, 6LX6, 6LX7, 6LX8, 6LX9, 6LXA, 6LXB, 6LXC, 7BPY, 7BPZ, 7BQ0, 7BQ1, 7BQ2, 7BQ3, 7BQ4 - PubMed Abstract:
Most triacylglycerol-lowering fibrates have been developed in the 1960s-1980s before their molecular target, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα), was identified. Twenty-one ligand-bound PPARα structures have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank since 2001; however, binding modes of fibrates and physiological ligands remain unknown. Here we show thirty-four X-ray crystallographic structures of the PPARα ligand-binding domain, which are composed of a "Center" and four "Arm" regions, in complexes with five endogenous fatty acids, six fibrates in clinical use, and six synthetic PPARα agonists. High-resolution structural analyses, in combination with coactivator recruitment and thermostability assays, demonstrate that stearic and palmitic acids are presumably physiological ligands; coordination to Arm III is important for high PPARα potency/selectivity of pemafibrate and GW7647; and agonistic activities of four fibrates are enhanced by the partial agonist GW9662. These results renew our understanding of PPARα ligand recognition and contribute to the molecular design of next-generation PPAR-targeted drugs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Health Chemistry, Showa Pharmaceutical University, Machida, Tokyo 194-8543, Japan.