Artificial Metalloproteins with Dinuclear Iron-Hydroxido Centers.
Miller, K.R., Biswas, S., Jasniewski, A., Follmer, A.H., Biswas, A., Albert, T., Sabuncu, S., Bominaar, E.L., Hendrich, M.P., Moenne-Loccoz, P., Borovik, A.S.(2021) J Am Chem Soc 143: 2384-2393
- PubMed: 33528256
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c12564
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
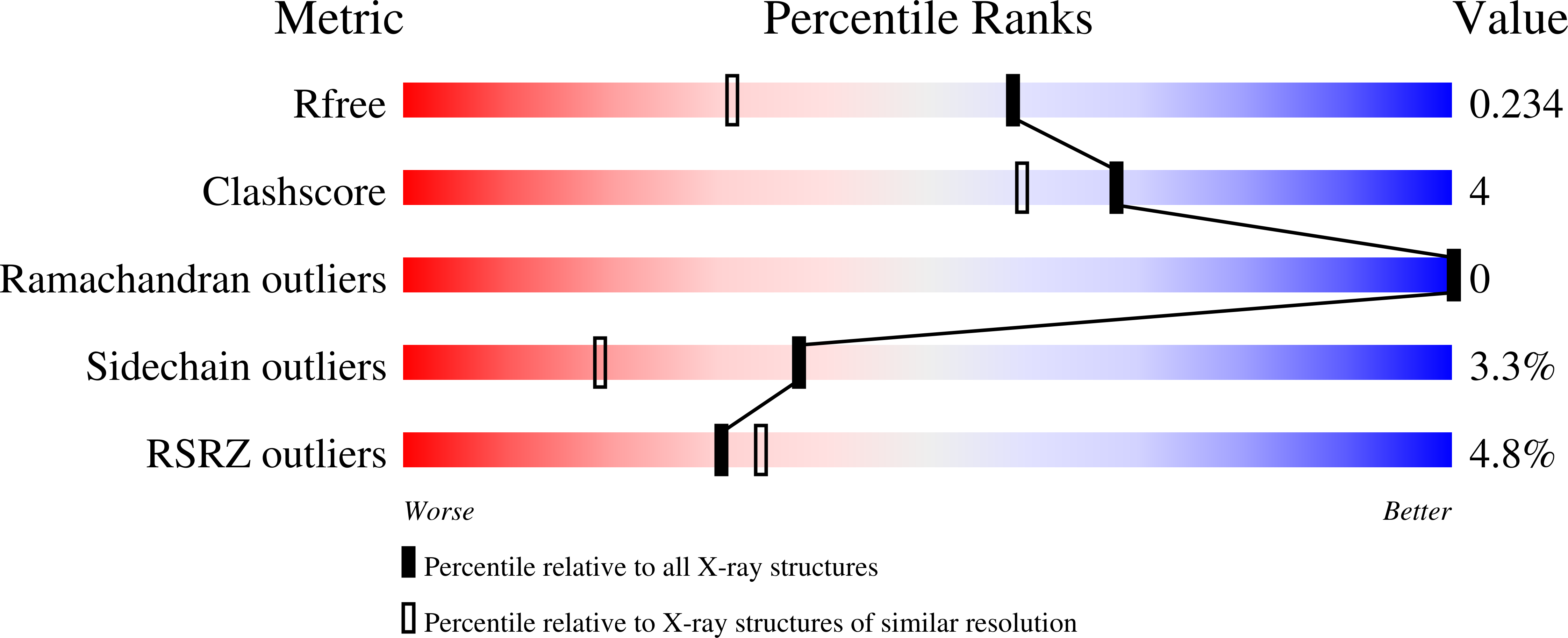
6VO9, 6VOB, 6VOZ, 6VP1, 6VP2, 6VP3, 7KBY, 7KBZ, 7KNL - PubMed Abstract:
Dinuclear iron centers with a bridging hydroxido or oxido ligand form active sites within a variety of metalloproteins. A key feature of these sites is the ability of the protein to control the structures around the Fe centers, which leads to entatic states that are essential for function. To simulate this controlled environment, artificial proteins have been engineered using biotin-streptavidin (Sav) technology in which Fe complexes from adjacent subunits can assemble to form [Fe III -(μ-OH)-Fe III ] cores. The assembly process is promoted by the site-specific localization of the Fe complexes within a subunit through the designed mutation of a tyrosinate side chain to coordinate the Fe centers. An important outcome is that the Sav host can regulate the Fe···Fe separation, which is known to be important for function in natural metalloproteins. Spectroscopic and structural studies from X-ray diffraction methods revealed uncommonly long Fe···Fe separations that change by less than 0.3 Å upon the binding of additional bridging ligands. The structural constraints imposed by the protein host on the di-Fe cores are unique and create examples of active sites having entatic states within engineered artificial metalloproteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, 1102 Natural Sciences II, University of California, Irvine, California 92697, United States.