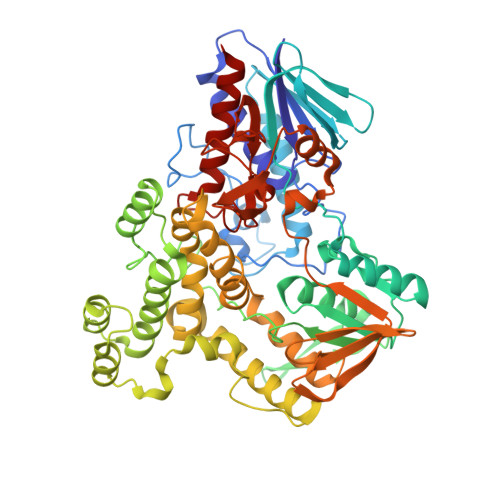
A biosynthetic aspartate N-hydroxylase performs successive oxidations by holding intermediates at a site away from the catalytic center.
Rotilio, L., Boverio, A., Nguyen, Q.T., Mannucci, B., Fraaije, M.W., Mattevi, A.(2023) J Biol Chem 299: 104904-104904
- PubMed: 37302552
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104904
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8CP2, 8CP5 - PubMed Abstract:
Nitrosuccinate is a biosynthetic building block in many microbial pathways. The metabolite is produced by dedicated L-aspartate hydroxylases that use NADPH and molecular oxygen as co-substrates. Here, we investigate the mechanism underlying the unusual ability of these enzymes to perform successive rounds of oxidative modifications. The crystal structure of Streptomyces sp. V2 L-aspartate N-hydroxylase outlines a characteristic helical domain wedged between two dinucleotide-binding domains. Together with NADPH and FAD, a cluster of conserved arginine residues forms the catalytic core at the domain interface. Aspartate is found to bind in an entry chamber that is close to but not in direct contact with the flavin. It is recognized by an extensive H-bond network that explains the enzyme's strict substrate-selectivity. A mutant designed to create steric and electrostatic hindrance to substrate binding disables hydroxylation without perturbing the NADPH oxidase side-activity. Critically, the distance between the FAD and the substrate is far too long to afford N-hydroxylation by the C4a-hydroperoxyflavin intermediate whose formation is confirmed by our work. We conclude that the enzyme functions through a catch-and-release mechanism. L-aspartate slides into the catalytic center only when the hydroxylating apparatus is formed. It is then re-captured by the entry chamber where it waits for the next round of hydroxylation. By iterating these steps, the enzyme minimizes the leakage of incompletely oxygenated products and ensures that the reaction carries on until nitrosuccinate is formed. This unstable product can then be engaged by a successive biosynthetic enzyme or undergoes spontaneous decarboxylation to produce 3-nitropropionate, a mycotoxin.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biology and Biotechnology, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy.