STX-478, a Mutant-Selective, Allosteric PI3K alpha Inhibitor Spares Metabolic Dysfunction and Improves Therapeutic Response in PI3K alpha-Mutant Xenografts.
Buckbinder, L., St Jean Jr., D.J., Tieu, T., Ladd, B., Hilbert, B., Wang, W., Alltucker, J.T., Manimala, S., Kryukov, G.V., Brooijmans, N., Dowdell, G., Jonsson, P., Huff, M., Guzman-Perez, A., Jackson, E.L., Goncalves, M.D., Stuart, D.D.(2023) Cancer Discov 13: 2432-2447
- PubMed: 37623743
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-23-0396
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
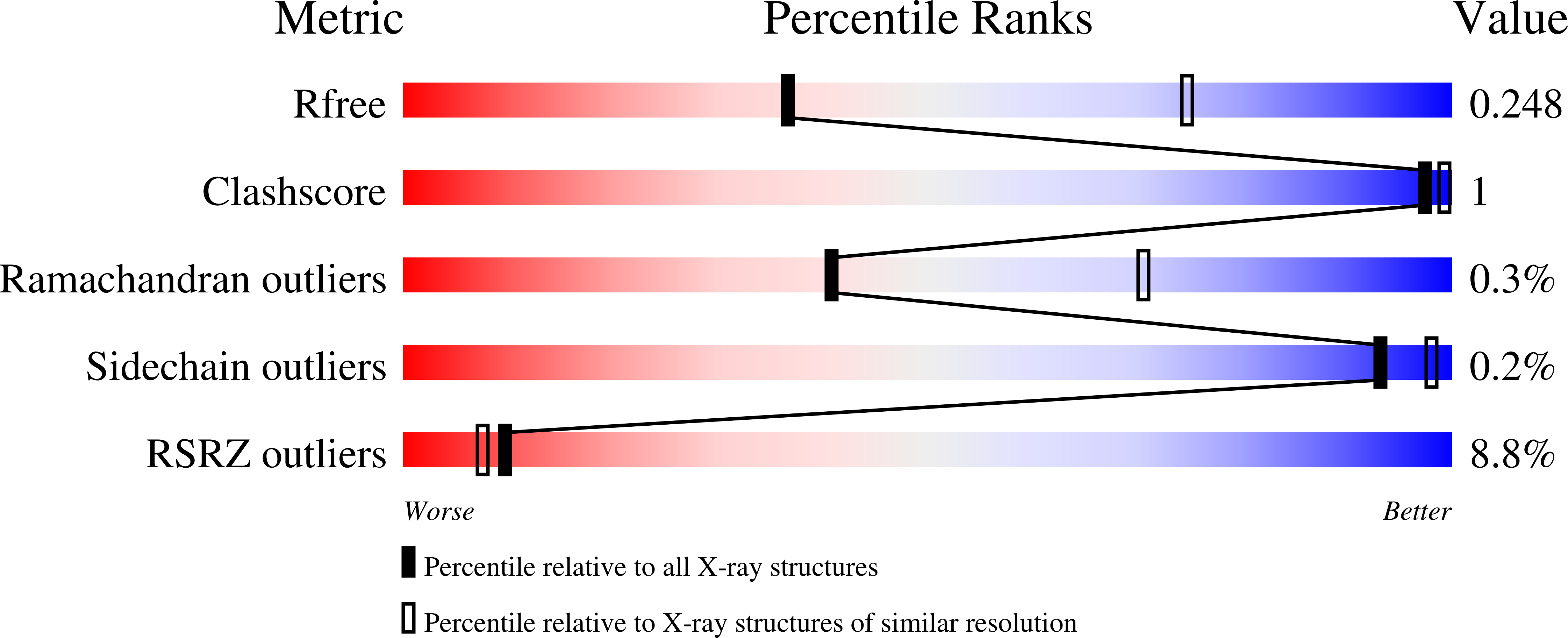
8TDU, 8TGD - PubMed Abstract:
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase α (PIK3CA) is one of the most mutated genes across cancers, especially breast, gynecologic, and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma tumors. Mutations occur throughout the gene, but hotspot mutations in the helical and kinase domains predominate. The therapeutic benefit of isoform-selective PI3Kα inhibition was established with alpelisib, which displays equipotent activity against the wild-type and mutant enzyme. Inhibition of wild-type PI3Kα is associated with severe hyperglycemia and rash, which limits alpelisib use and suggests that selectively targeting mutant PI3Kα could reduce toxicity and improve efficacy. Here we describe STX-478, an allosteric PI3Kα inhibitor that selectively targets prevalent PI3Kα helical- and kinase-domain mutant tumors. STX-478 demonstrated robust efficacy in human tumor xenografts without causing the metabolic dysfunction observed with alpelisib. Combining STX-478 with fulvestrant and/or cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors was well tolerated and provided robust and durable tumor regression in ER+HER2- xenograft tumor models. These preclinical data demonstrate that the mutant-selective, allosteric PI3Kα inhibitor STX-478 provides robust efficacy while avoiding the metabolic dysfunction associated with the nonselective inhibitor alpelisib. Our results support the ongoing clinical evaluation of STX-478 in PI3Kα-mutated cancers, which is expected to expand the therapeutic window and mitigate counterregulatory insulin release. See related commentary by Kearney and Vasan, p. 2313. This article is featured in Selected Articles from This Issue, p. 2293.
Organizational Affiliation:
Research and Development, Scorpion Therapeutics, Boston, Massachusetts.