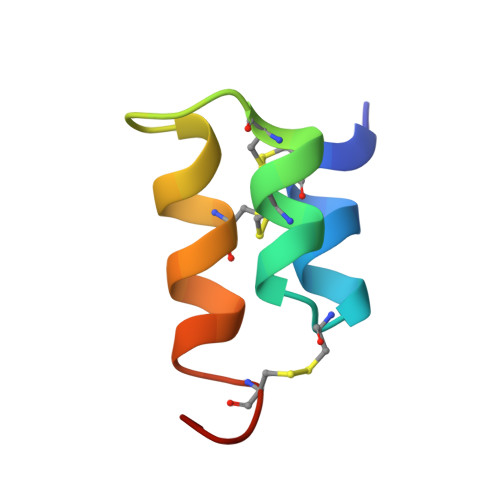
The NMR solution structure of the pheromone Er-1 from the ciliated protozoan Euplotes raikovi.
Mronga, S., Luginbuhl, P., Brown, L.R., Ortenzi, C., Luporini, P., Bradshaw, R.A., Wuthrich, K.(1994) Protein Sci 3: 1527-1536
- PubMed: 7833812
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.5560030918
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1ERC - PubMed Abstract:
The 3-dimensional structure of the pheromone Er-1 isolated from the ciliated protozoan Euplotes raikovi has been determined in aqueous solution by 1H NMR spectroscopy. The structure of this 40-residue protein was calculated with the distance geometry program DIANA on the basis of 503 upper distance constraints derived from nuclear Overhauser effects and 77 dihedral angle constraints derived from spin-spin coupling constants, and refined by restrained energy minimization with the program OPAL. The Er-1 solution structure is represented by a group of 20 conformers with an average RMS deviation relative to the mean structure of 0.55 A for the backbone atoms N, C alpha, and C', and 0.93 A for all heavy atoms of the complete polypeptide chain, residues 1-40. The molecular architecture is dominated by an up-down-up bundle of 3 alpha-helices formed by residues 2-9, 12-19, and 24-33. Although this core part coincides closely with the previously determined structure of the homologous pheromone Er-10, the C-terminal peptide segment adopts a novel conformation. This is of interest in view of previous suggestions, based on sequence comparisons, that this molecular region may be important for the different specificity of receptor recognition by different pheromones.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut für Molekularbiologie und Biophysik, Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule, Zürich, Switzerland.