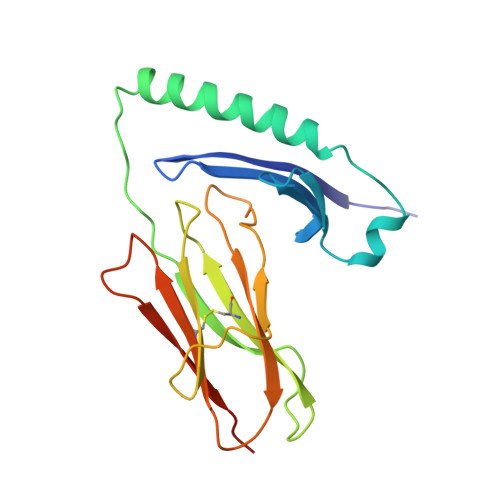
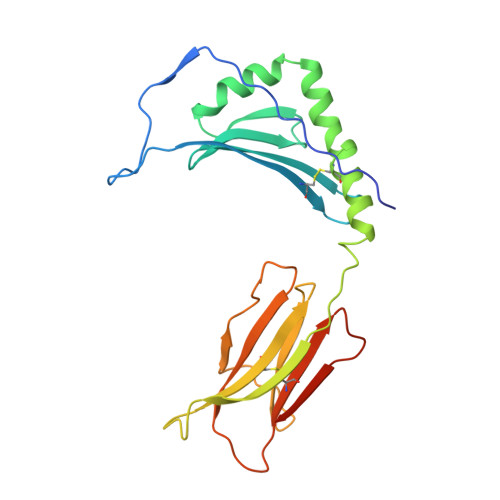
Structures of an MHC class II molecule with covalently bound single peptides.
Fremont, D.H., Hendrickson, W.A., Marrack, P., Kappler, J.(1996) Science 272: 1001-1004
- PubMed: 8638119
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.272.5264.1001
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1IEA, 1IEB - PubMed Abstract:
The high-resolution x-ray crystal structures of the murine major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecule, I-E(k), occupied by either of two antigenic peptides were determined. They reveal the structural basis for the I-E(k) peptide binding motif and suggest general principles for additional alleles. A buried cluster of acidic amino acids in the binding groove predicted to be conserved among all murine I-E and human DR MHC class II molecules suggests how pH may influence MHC binding or exchange of peptides. These structures also complement mutational studies on the importance of individual peptide residues to T cell receptor recognition.
Organizational Affiliation:
Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics, Columbia University, New York, 10032, USA.