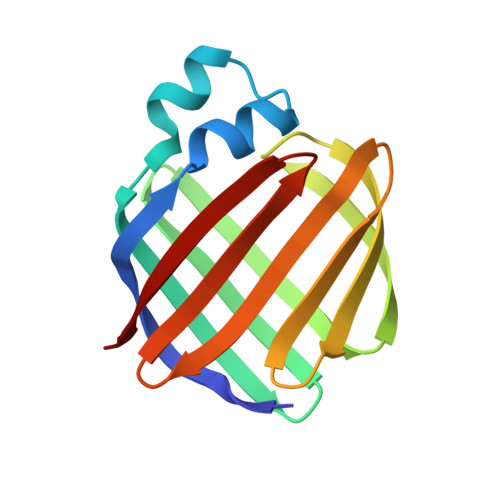
Crystal structures of holo and apo-cellular retinol-binding protein II.
Winter, N.S., Bratt, J.M., Banaszak, L.J.(1993) J Mol Biol 230: 1247-1259
- PubMed: 8487303
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1993.1239
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1OPA, 1OPB - PubMed Abstract:
Apo and holo-cellular retinol-binding protein II have been crystallized, and their crystal structures have been determined to 2.1 A and 1.9 A respectively. The apo and holo-crystals have different but related triclinic space groups. The X-ray phases for both structures were determined using the molecular replacement method. The crystal co-ordinates were refined to an R-factor of 0.200 for apo, and 0.173 for holo-cellular retinol-binding protein II. The holo and apo-models have nearly the same tertiary structures. Cellular retinol-binding protein II consists of a ten-stranded anti-parallel beta-barrel with the ligand binding cavity within the barrel. Two alpha-helices cover the open end of the beta-barrel making it almost solvent inaccessible. A single portal large enough to admit a water molecule was observed opening into the binding cavity. Exogenously added retinol was found within the cavity of each holo-cellular retinol-binding protein II molecule. Each retinol was surrounded by both polar and non-polar residues. The hydroxyl group of the bound retinol hydrogen bonds to the amide group of glutamine 108. The overall conformation of the bound retinol was derived from the four different molecules of holo-cellular retinol-binding protein II present in the triclinic form. The four copies of bound retinol had essentially the same conformation as found in crystalline retinaldehyde.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Medical School, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis 55455.