The design and synthesis of human branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase inhibitors for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
Hu, L.Y., Boxer, P.A., Kesten, S.R., Lei, H.J., Wustrow, D.J., Moreland, D.W., Zhang, L., Ahn, K., Ryder, T.R., Liu, X., Rubin, J.R., Fahnoe, K., Carroll, R.T., Dutta, S., Fahnoe, D.C., Probert, A.W., Roof, R.L., Rafferty, M.F., Kostlan, C.R., Scholten, J.D., Hood, M., Ren, X.D., Schielke, G.P., Su, T.Z., Taylor, C.P., Mistry, A., McConnell, P., Hasemann, C., Ohren, J.(2006) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16: 2337-2340
- PubMed: 16143519
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.07.058
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
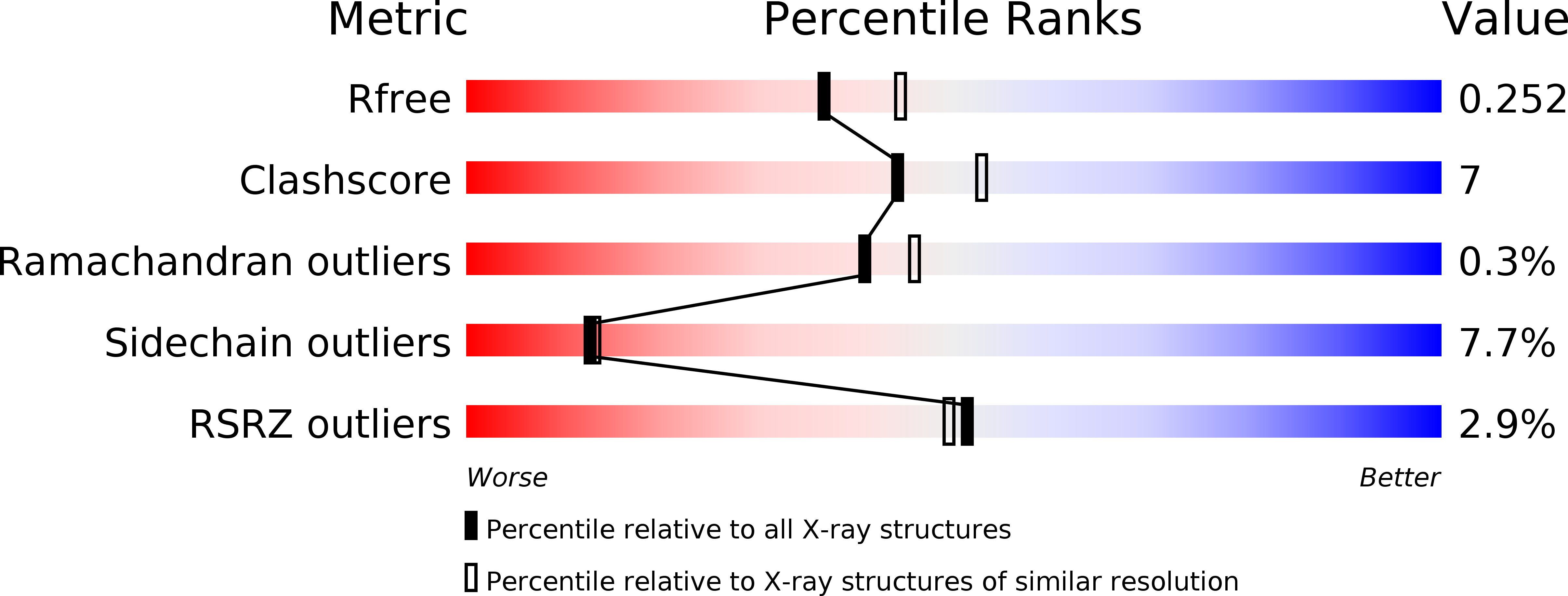
2ABJ - PubMed Abstract:
The inhibition of the cytosolic isoenzyme BCAT that is expressed specifically in neuronal tissue is likely to be useful for the treatment of neurodegenerative and other neurological disorders where glutamatergic mechanisms are implicated. Compound 2 exhibited an IC50 of 0.8 microM in the hBCATc assays; it is an active and selective inhibitor. Inhibitor 2 also blocked calcium influx into neuronal cells following inhibition of glutamate uptake, and demonstrated neuroprotective efficacy in vivo. SAR, pharmacology, and the crystal structure of hBCATc with inhibitor 2 are described.
Organizational Affiliation:
Pfizer Global Research and Development, Ann Arbor, MI, USA. [email protected]