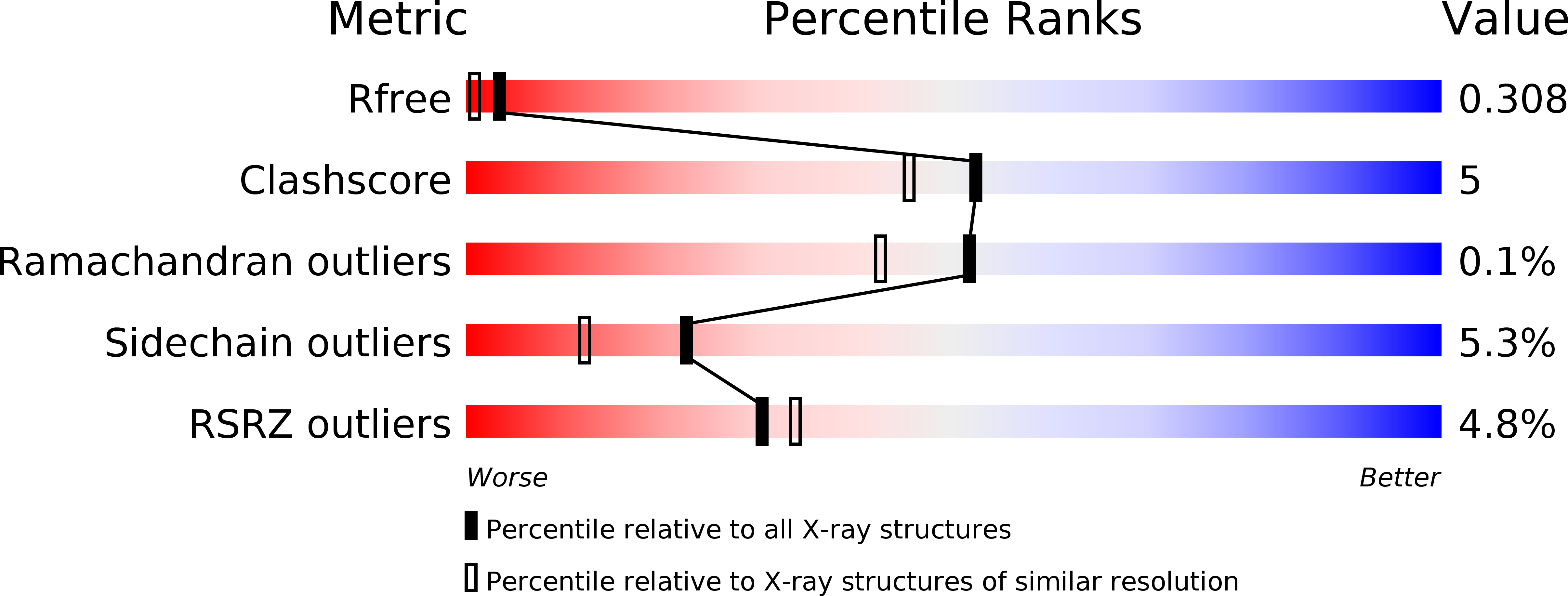
Development of potent, orally active 1-substituted-3,4-dihydro-2-quinolone glycogen phosphorylase inhibitors.
Birch, A.M., Kenny, P.W., Oikonomakos, N.G., Otterbein, L., Schofield, P., Whittamore, P.R., Whalley, D.P.(2007) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17: 394-399
- PubMed: 17095214
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.10.037
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2IEG, 2IEI - PubMed Abstract:
A series of substituted 3,4-dihydro-2-quinolone glycogen phosphorylase inhibitors, which have potential as antidiabetic agents, is described. Initial members of the series showed good enzyme inhibitory potency but poor physical properties. Optimisation of the 1-substituent led to 2,3-dihydroxypropyl compounds which showed good in vitro potency and improved physical properties, together with good DMPK profiles and acute in vivo efficacy in a rat model. X-ray crystallographic data are presented, showing an unexpected variety of binding orientations at the dimer interface site.
Organizational Affiliation:
AstraZeneca, Mereside, Alderley Park, Macclesfield, Cheshire SK10 4TG, UK. [email protected]