Design, Synthesis, and Activity of 2-Imidazol-1-ylpyrimidine Derived Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Dimerization Inhibitors
Davey, D.D., Adler, M., Arnaiz, D., Eagen, K., Erickson, S., Guilford, W., Kenrick, M., Morrissey, M.M., Ohlmeyer, M., Pan, G., Paradkar, V.M., Parkinson, J., Polokoff, M., Saionz, K., Santos, C., Subramanyam, B., Vergona, R., Wei, R.G., Whitlow, M., Ye, B., Zhao, Z.S., Devlin, J.J., Phillips, G.(2007) J Med Chem 50: 1146-1157
- PubMed: 17315988
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm061319i
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
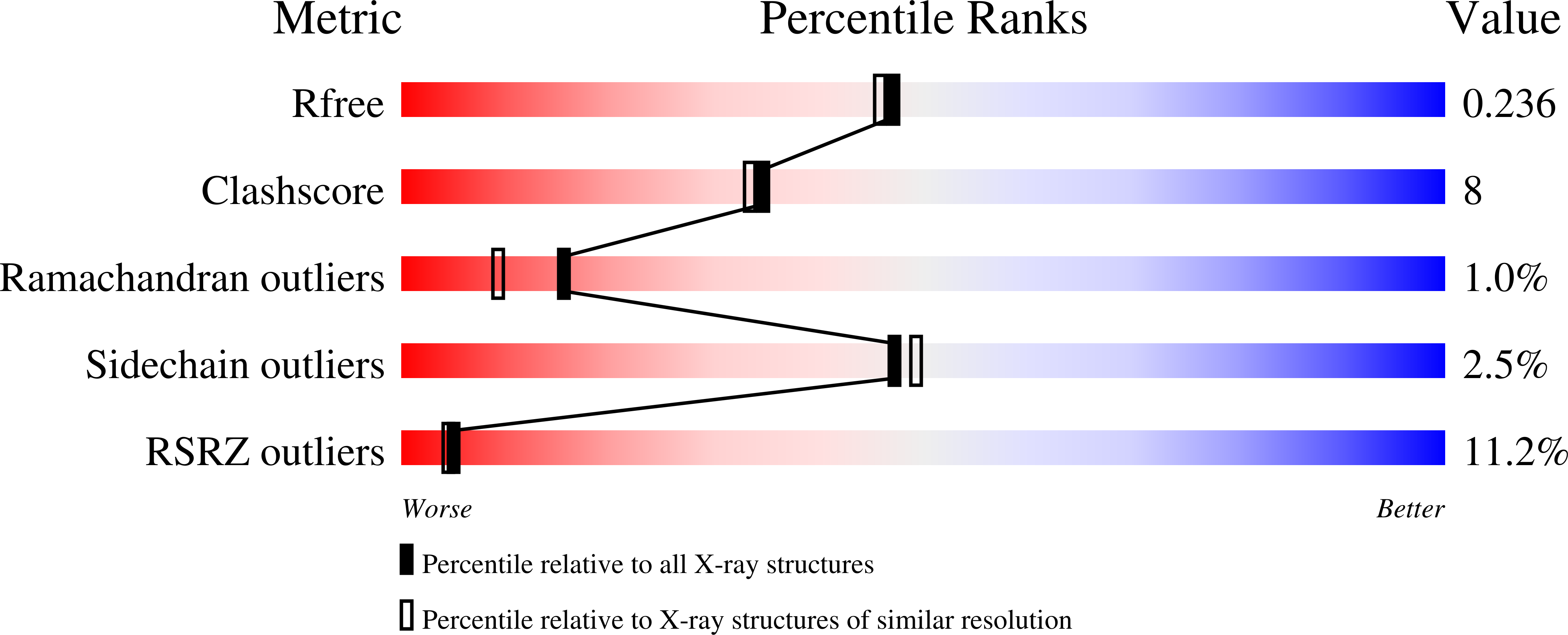
2ORO, 2ORP, 2ORQ, 2ORR, 2ORS, 2ORT - PubMed Abstract:
By the screening of a combinatorial library for inhibitors of nitric oxide (NO) formation by the inducible isoform of nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) using a whole-cell assay, 2-(imidazol-1-yl)pyrimidines were identified. Compounds were found to inhibit the dimerization of iNOS monomers, thus preventing the formation of the dimeric, active form of the enzyme. Optimization led to the selection of the potent, selective, and orally available iNOS dimerization inhibitor, 21b, which significantly ameliorated adjuvant-induced arthritis in a rat model. Analysis of the crystal structure of the 21b--iNOS monomer complex provided a rationalization for both the SAR and the mechanism by which 21b blocks the formation of the protein--protein interaction present in the dimeric form of iNOS.
Organizational Affiliation:
Berlex Biosciences, 2600 Hilltop Drive, P.O. Box 4099, Richmond, California 94804-0099, USA.