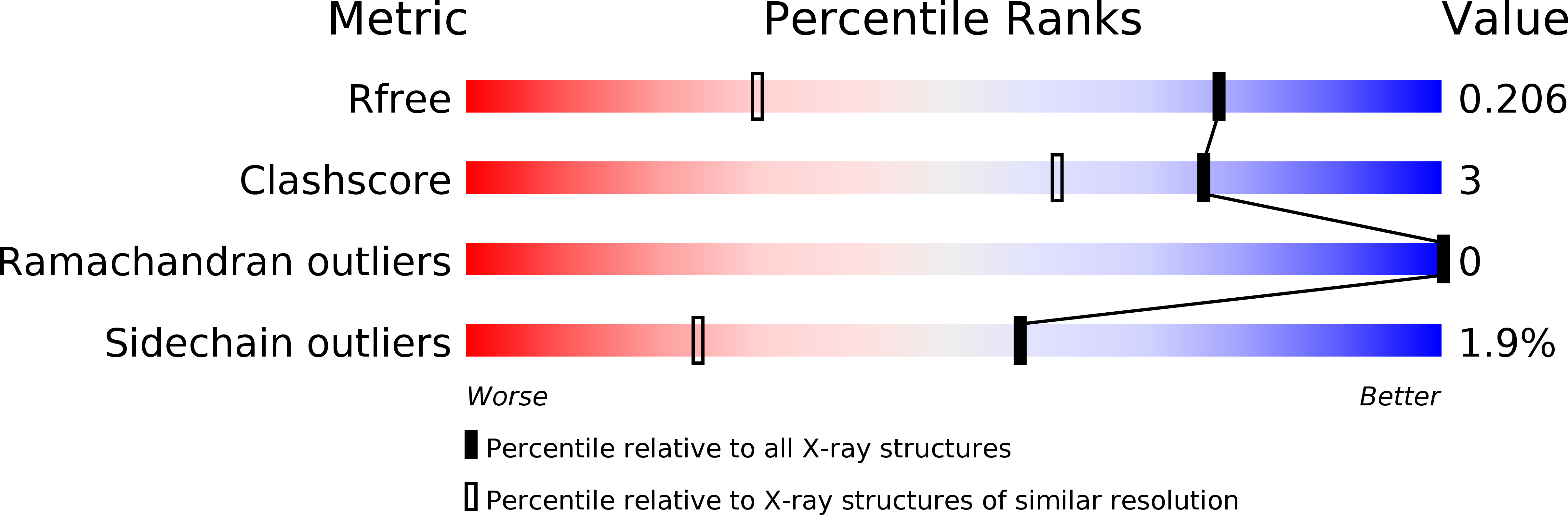
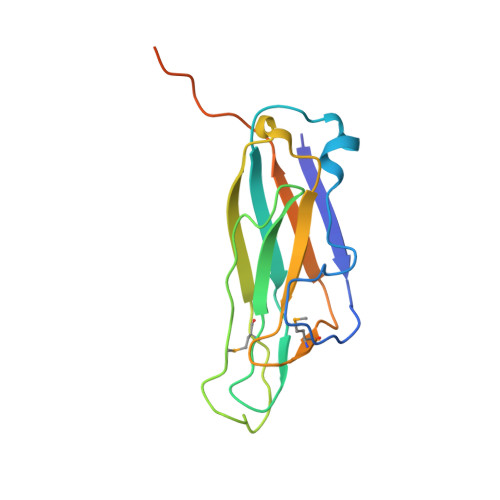
A Tnf-Like Trimeric Lectin Domain from Burkholderia Cenocepacia with Specificity for Fucosylated Human Histo-Blood Group Antigens
Sulak, O., Cioci, G., Lahman, M., Delia, M., Varrot, A., Imberty, A., Wimmerova, M.(2010) Structure 18: 59
- PubMed: 20152153
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2009.10.021
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2WQ4 - PubMed Abstract:
The opportunistic pathogen Burkholderia cenocepacia expresses several soluble lectins, among them BC2L-C. This lectin exhibits two domains: a C-terminal domain with high sequence similarity to the recently described calcium-dependent mannose-binding lectin BC2L-A, and an N-terminal domain of 156 amino acids without similarity to any known protein. The recombinant N-terminal BC2L-C domain is a new lectin with specificity for fucosylated human histo-blood group epitopes H-type 1, Lewis b, and Lewis Y, as determined by glycan array and isothermal titration calorimetry. Methylselenofucoside was used as ligand to solve the crystal structure of the N-terminal BC2L-C domain. Additional molecular modeling studies rationalized the preference for Lewis epitopes. The structure reveals a trimeric jellyroll arrangement with striking similarity to TNF-like proteins, and to BclA, the spore protein from Bacillus anthracis which may play an important role in bioadhesion of anthrax spores in human lungs.
Organizational Affiliation:
National Centre for Biomolecular Research, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Kotlárská 2, 611 37 Brno, Czech Republic.