The Ternary Complex of Prnb (the Second Enzyme in Pyrrolnitrin Biosynthesis Pathway), Tryptophan and Cyanide Yields New Mechanistic Insights Into the Indolamine Dioxygenase Superfamily.
Zhu, X., Van Pee, K.-H., Naismith, J.H.(2010) J Biol Chem 285: 21126
- PubMed: 20421301
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.120485
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2X66, 2X67, 2X68 - PubMed Abstract:
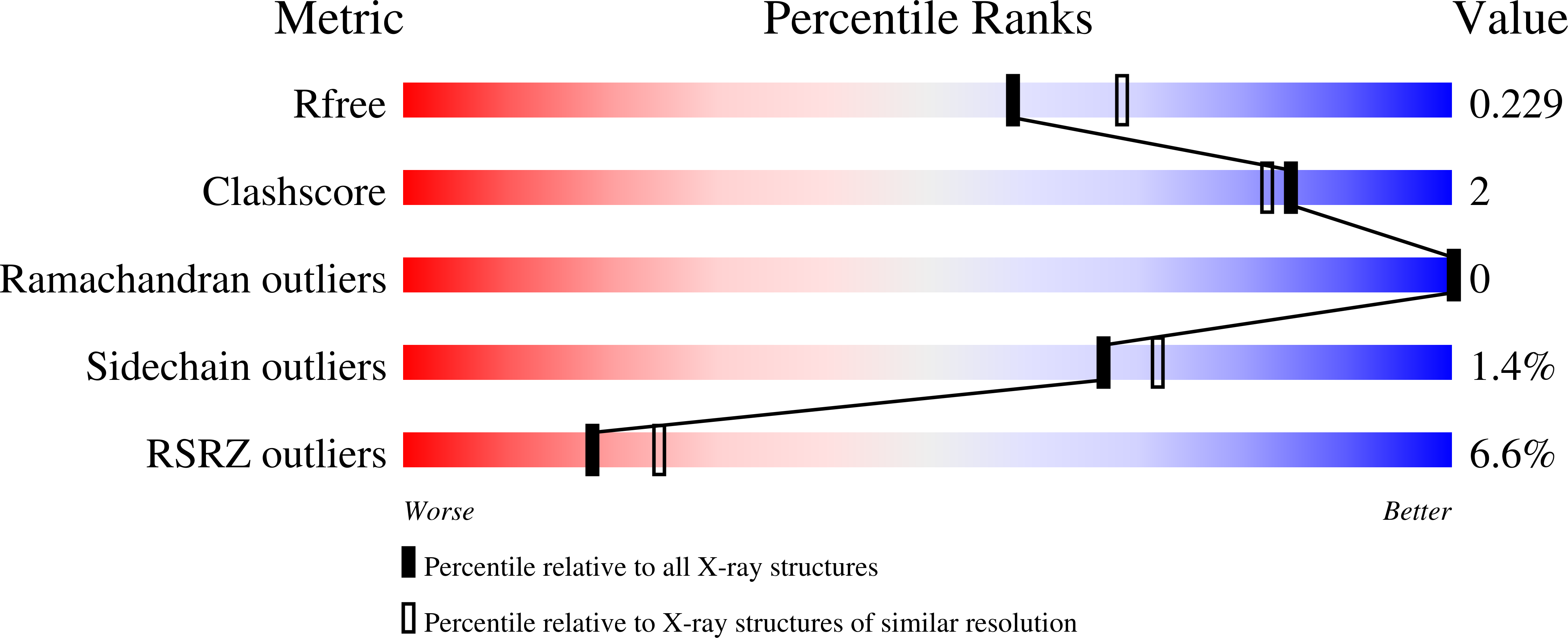
Pyrrolnitrin (3-chloro-4-(2'-nitro-3'-chlorophenyl)pyrrole) is a broad-spectrum antifungal compound isolated from Pseudomonas pyrrocinia. Four enzymes (PrnA, PrnB, PrnC, and PrnD) are required for pyrrolnitrin biosynthesis from tryptophan. PrnB rearranges the indole ring of 7-Cl-l-tryptophan and eliminates the carboxylate group. PrnB shows robust activity in vivo, but in vitro activity for PrnB under defined conditions remains undetected. The structure of PrnB establishes that the enzyme belongs to the heme b-dependent indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) and tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO) family. We report the cyanide complex of PrnB and two ternary complexes with both l-tryptophan or 7-Cl-l-tryptophan and cyanide. The latter two complexes are essentially identical and mimic the likely catalytic ternary complex that occurs during turnover. In the cyanide ternary complexes, a loop previously disordered becomes ordered, contributing to the binding of substrates. The conformations of the bound tryptophan substrates are changed from that seen previously in the binary complexes. In l-tryptophan ternary complex, the indole ring now adopts the same orientation as seen in the PrnB binary complexes with other tryptophan substrates. The amide and carboxylate group of the substrate are orientated in a new conformation. Tyr(321) and Ser(332) play a key role in binding these groups. The structures suggest that catalysis requires an l-configured substrate. Isothermal titration calorimetry data suggest d-tryptophan does not bind after cyanide (or oxygen) coordinates with the distal (or sixth) site of heme. This is the first ternary complex with a tryptophan substrate of a member of the tryptophan dioxygenase superfamily and has mechanistic implications.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biomedical Sciences Research Complex, University of St. Andrews, St. Andrews KY16 9ST, Scotland, United Kingdom.