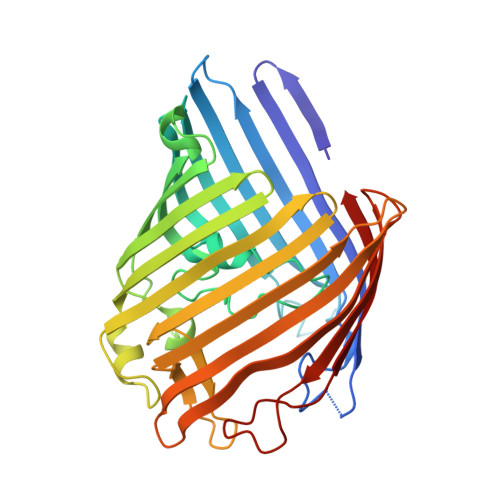
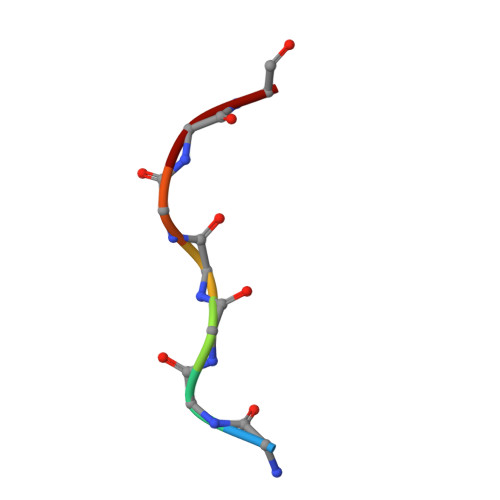
Crystal structures of the OmpF porin: function in a colicin translocon.
Yamashita, E., Zhalnina, M.V., Zakharov, S.D., Sharma, O., Cramer, W.A.(2008) EMBO J 27: 2171-2180
- PubMed: 18636093
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2008.137
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2ZFG, 2ZLD - PubMed Abstract:
The OmpF porin in the Escherichia coli outer membrane (OM) is required for the cytotoxic action of group A colicins, which are proposed to insert their translocation and active domains through OmpF pores. A crystal structure was sought of OmpF with an inserted colicin segment. A 1.6 A OmpF structure, obtained from crystals formed in 1 M Mg2+, has one Mg2+ bound in the selectivity filter between Asp113 and Glu117 of loop 3. Co-crystallization of OmpF with the unfolded 83 residue glycine-rich N-terminal segment of colicin E3 (T83) that occludes OmpF ion channels yielded a 3.0 A structure with inserted T83, which was obtained without Mg2+ as was T83 binding to OmpF. The incremental electron density could be modelled as an extended poly-glycine peptide of at least seven residues. It overlapped the Mg2+ binding site obtained without T83, explaining the absence of peptide binding in the presence of Mg2+. Involvement of OmpF in colicin passage through the OM was further documented by immuno-extraction of an OM complex, the colicin translocon, consisting of colicin E3, BtuB and OmpF.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47907-1392, USA.