Metal active site elasticity linked to activation of homocysteine in methionine synthases.
Koutmos, M., Pejchal, R., Bomer, T.M., Matthews, R.G., Smith, J.L., Ludwig, M.L.(2008) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105: 3286-3291
- PubMed: 18296644
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0709960105
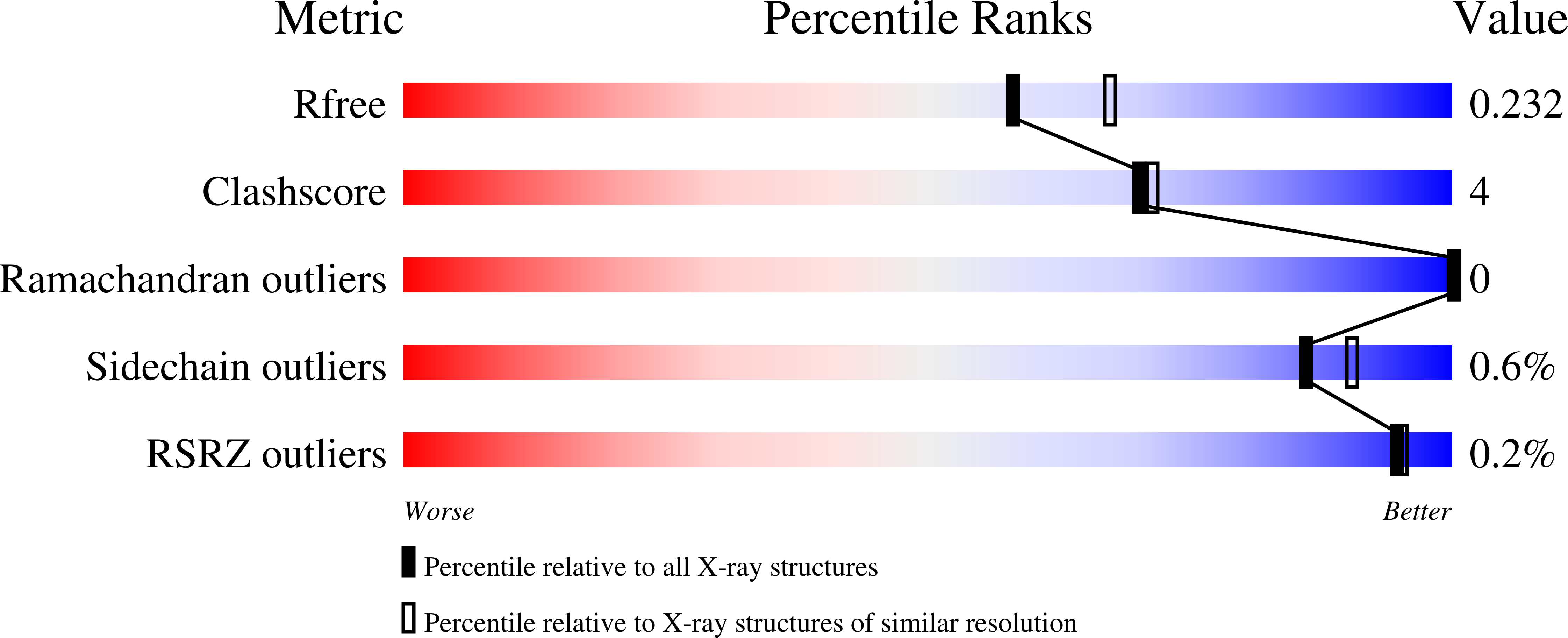
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3BOF, 3BOL, 3BQ5, 3BQ6 - PubMed Abstract:
Enzymes possessing catalytic zinc centers perform a variety of fundamental processes in nature, including methyl transfer to thiols. Cobalamin-independent (MetE) and cobalamin-dependent (MetH) methionine synthases are two such enzyme families. Although they perform the same net reaction, transfer of a methyl group from methyltetrahydrofolate to homocysteine (Hcy) to form methionine, they display markedly different catalytic strategies, modular organization, and active site zinc centers. Here we report crystal structures of zinc-replete MetE and MetH, both in the presence and absence of Hcy. Structural investigation of the catalytic zinc sites of these two methyltransferases reveals an unexpected inversion of zinc geometry upon binding of Hcy and displacement of an endogenous ligand in both enzymes. In both cases a significant movement of the zinc relative to the protein scaffold accompanies inversion. These structures provide new information on the activation of thiols by zinc-containing enzymes and have led us to propose a paradigm for the mechanism of action of the catalytic zinc sites in these and related methyltransferases. Specifically, zinc is mobile in the active sites of MetE and MetH, and its dynamic nature helps facilitate the active site conformational changes necessary for thiol activation and methyl transfer.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biophysics Research Division, Life Sciences Institute, and Department of Biological Chemistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109, USA. [email protected]