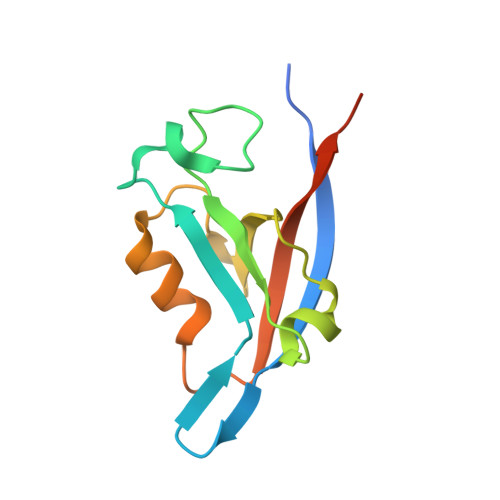
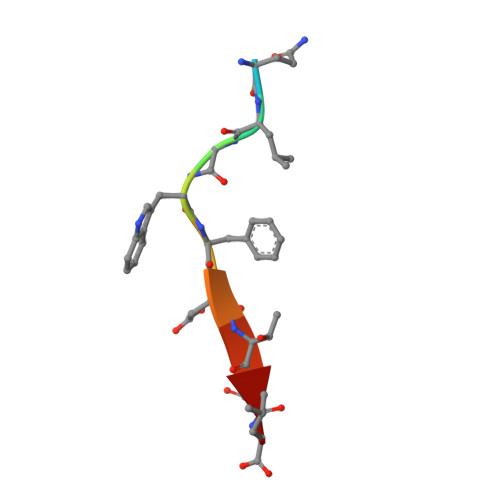
Structural Basis of beta-Catenin Recognition by Tax-interacting Protein-1
Zhang, J., Yan, X., Shi, C., Yang, X., Guo, Y., Tian, C., Long, J., Shen, Y.(2008) J Mol Biol 384: 255-263
- PubMed: 18835279
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.09.034
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3DIW, 3DJ1, 3DJ3 - PubMed Abstract:
Tax-interacting protein-1 (TIP-1) is an unusual signaling protein, containing a single PDZ domain. TIP-1 is able to bind beta-catenin with high affinity and thus inhibit its transcriptional activity. The high-resolution crystal structure of TIP-1 in complex with the C-terminal peptide of beta-catenin provides molecular details for the recognition of beta-catenin by TIP-1. Moreover, structural comparison of peptide-free and peptide-bound TIP-1 reveals that significant conformational changes are required in the betaB-betaC loop region of TIP-1 to avoid clashes with the incoming C-terminal beta-catenin peptide. Such conformational changes have not been observed in other structures of PDZ domains. In addition to the canonical peptide-binding pocket of the PDZ domain, TIP-1 can form a binding cavity to anchor more amino acids through a conserved hydrophobic residue pair (Trp776 of beta-catenin and Pro45 of TIP-1). Structural and biochemical data indicate that the canonical binding pocket together with the hydrophobic residue pair are presumably the major cause of the significantly higher affinity of the beta-catenin C-terminal to TIP-1 than to other PDZ domains, providing a unique binding specificity. Our results reveal the molecular mechanism of TIP-1 as an antagonist in PDZ domain signaling.
Organizational Affiliation:
Tianjin Key Laboratory of Protein Science, College of Life Science, NanKai University, Tianjin 300071, China.