Biochemical and structural study of the atypical acyltransferase domain from the mycobacterial polyketide synthase pks13
Bergeret, F., Gavalda, S., Chalut, C., Malaga, W., Quemard, A., Pedelacq, J.D., Daffe, M., Guilhot, C., Mourey, L., Bon, C.(2012) J Biol Chem 287: 33675-33690
- PubMed: 22825853
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.325639
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3TZW, 3TZX, 3TZY, 3TZZ - PubMed Abstract:
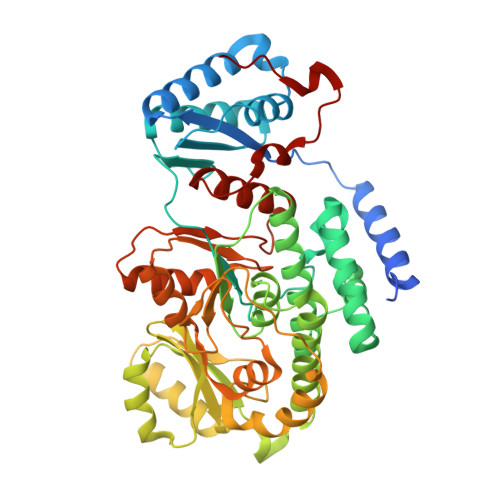
Pks13 is a type I polyketide synthase involved in the final biosynthesis step of mycolic acids, virulence factors, and essential components of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis envelope. Here, we report the biochemical and structural characterization of a 52-kDa fragment containing the acyltransferase domain of Pks13. This fragment retains the ability to load atypical extender units, unusually long chain acyl-CoA with a predilection for carboxylated substrates. High resolution crystal structures were determined for the apo, palmitoylated, and carboxypalmitoylated forms. Structural conservation with type I polyketide synthases and related fatty-acid synthases also extends to the interdomain connections. Subtle changes could be identified both in the active site and in the upstream and downstream linkers in line with the organization displayed by this singular polyketide synthase. More importantly, the crystallographic analysis illustrated for the first time how a long saturated chain can fit in the core structure of an acyltransferase domain through a dedicated channel. The structures also revealed the unexpected binding of a 12-mer peptide that might provide insight into domain-domain interaction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut de Pharmacologie et de Biologie Structurale (IPBS), CNRS, Toulouse, France.