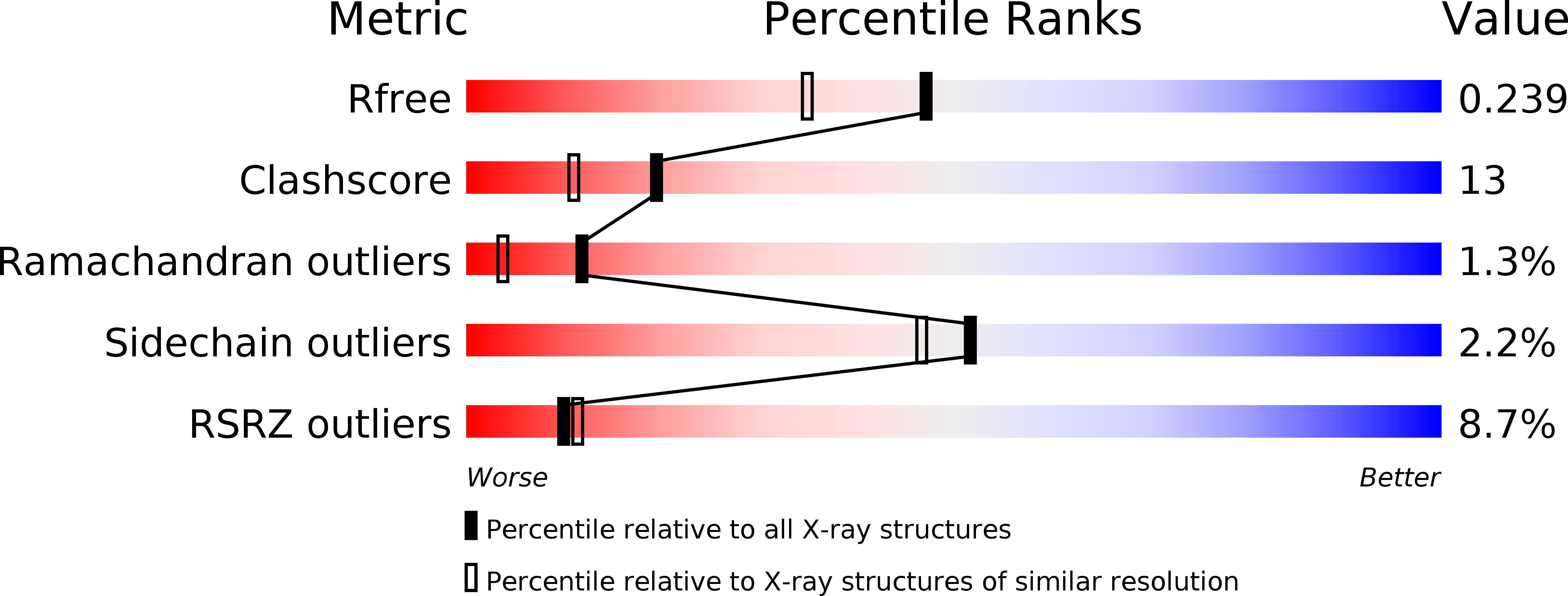
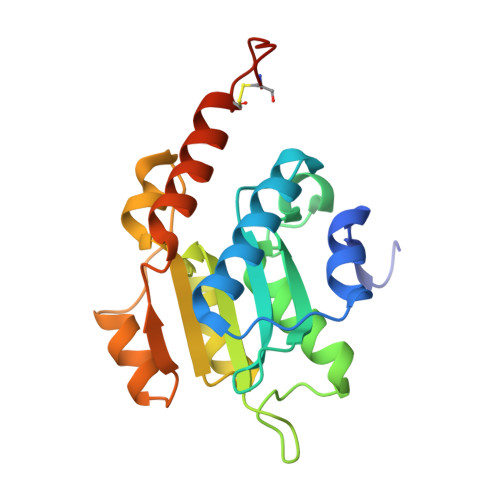
Identification of function and mechanistic insights of guanine deaminase from Nitrosomonas europaea: role of the C-terminal loop in catalysis
Bitra, A., Hussain, B., Tanwar, A.S., Anand, R.(2013) Biochemistry 52: 3512-3522
- PubMed: 23557066
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi400068g
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4HRQ, 4HRW - PubMed Abstract:
NE0047 from Nitrosomonas europaea has been annotated as a zinc-dependent deaminase; however, the substrate specificity is unknown because of the low level of structural similarity and sequence identity compared to other family members. In this study, the function of NE0047 was established as a guanine deaminase (catalytic efficiency of 1.2 × 10(5) M(-1) s(-1)), exhibiting secondary activity towards ammeline. The structure of NE0047 in the presence of the substrate analogue 8-azaguanine was also determined to a resolution of 1.9 Å. NE0047 crystallized as a homodimer in an asymmetric unit. It was found that the extreme nine-amino acid C-terminal loop forms an active site flap; in one monomer, the flap is in the closed conformation and in the other in the open conformation with this loop region exposed to the solvent. Calorimetric data obtained using the full-length version of the enzyme fit to a sequential binding model, thus supporting a cooperative mode of ligand occupancy. In contrast, the mutant form of the enzyme (ΔC) with the deletion of the extreme nine amino acids follows an independent model of ligand occupancy. In addition, the ΔC mutant also does not exhibit any enzyme activity. Therefore, we propose that the progress of the reaction is communicated via changes in the conformation of the C-terminal flap and the closed form of the enzyme is the catalytically active form, while the open form allows for product release. The catalytic mechanism of deamination was also investigated, and we found that the mutagenesis of the highly conserved active site residues Glu79 and Glu143 resulted in a complete loss of activity and concluded that they facilitate the reaction by serving as proton shuttles.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, IIT Bombay , Mumbai, India 400076.