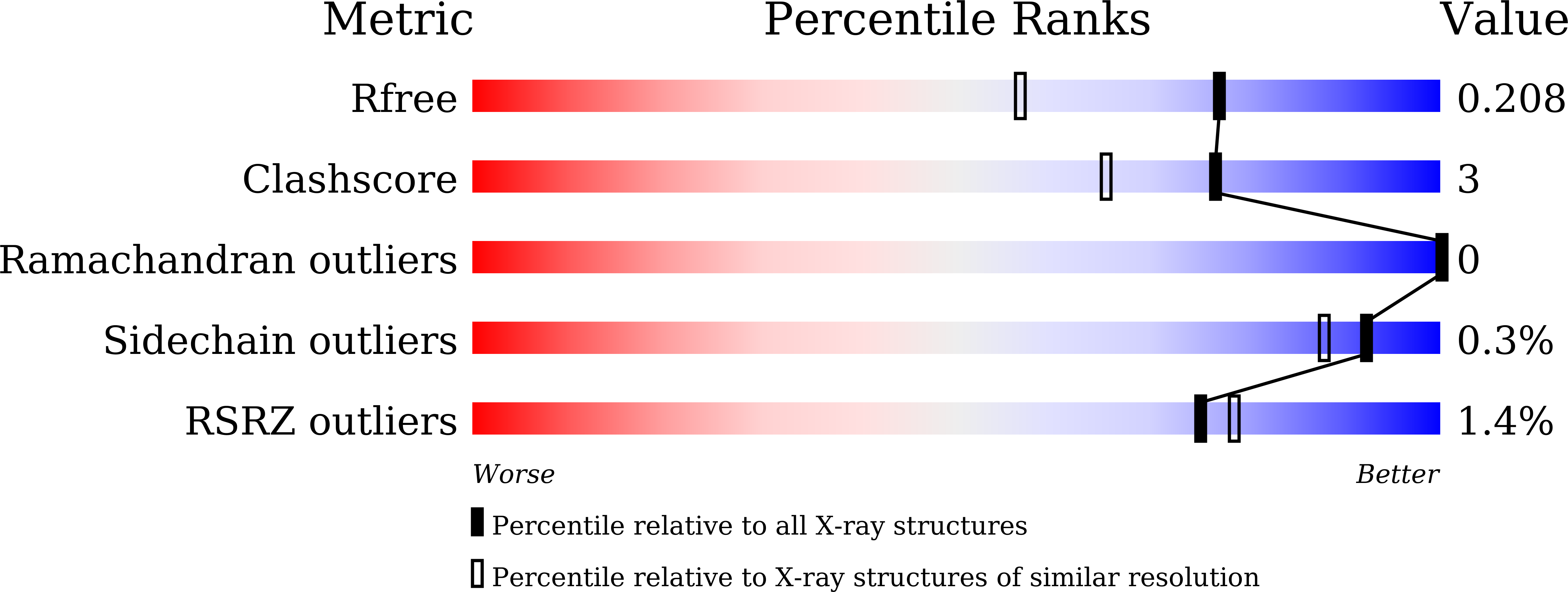
Structural Basis for the Catalytic Mechanism of DncV, Bacterial Homolog of Cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase
Kato, K., Ishii, R., Hirano, S., Ishitani, R., Nureki, O.(2015) Structure 23: 843-850
- PubMed: 25865248
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2015.01.023
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4XJ1, 4XJ3, 4XJ4, 4XJ5, 4XJ6 - PubMed Abstract:
Cyclic dinucleotides (CDNs) play key roles as second messengers and signaling molecules in bacteria and metazoans. The newly identified dinucleotide cyclase in Vibrio cholerae (DncV) produces three different CDNs containing two 3'-5' phosphodiester bonds, and its predominant product is cyclic GMP-AMP, whereas mammalian cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) produces only cyclic GMP-AMP containing mixed 2'-5' phosphodiester bonds. We report the crystal structures of V. cholerae and Escherichia coli DncV in complex with various nucleotides in the pre-reaction states. The high-resolution structures revealed that DncV preferably recognizes ATP and GTP as acceptor and donor nucleotides, respectively, in the first nucleotidyl transfer reaction. Considering the recently reported intermediate structures, our pre-reaction state structures provide the precise mechanism of 3'-5' linked cyclic AMP-GMP production in bacteria. A comparison with cGAS in the pre-reaction states suggests that the orientation of the acceptor nucleotide primarily determines the distinct linkage specificities between DncV and cGAS.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0032, Japan.