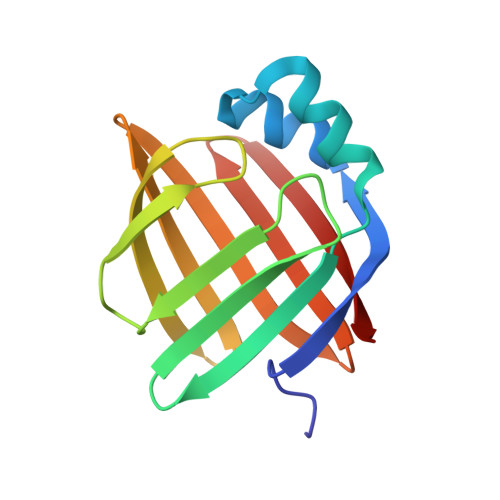
Structural basis for the ligand-binding specificity of fatty acid-binding proteins (pFABP4 and pFABP5) in gentoo penguin
Lee, C.W., Kim, J.E., Do, H., Kim, R.O., Lee, S.G., Park, H.H., Chang, J.H., Yim, J.H., Park, H., Kim, I.C., Lee, J.H.(2015) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 465: 12-18
- PubMed: 26206084
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.07.087
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5BVQ, 5BVS, 5BVT - PubMed Abstract:
Fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs) are involved in transporting hydrophobic fatty acids between various aqueous compartments of the cell by directly binding ligands inside their β-barrel cavities. Here, we report the crystal structures of ligand-unbound pFABP4, linoleate-bound pFABP4, and palmitate-bound pFABP5, obtained from gentoo penguin (Pygoscelis papua), at a resolution of 2.1 Å, 2.2 Å, and 2.3 Å, respectively. The pFABP4 and pFABP5 proteins have a canonical β-barrel structure with two short α-helices that form a cap region and fatty acid ligand binding sites in the hydrophobic cavity within the β-barrel structure. Linoleate-bound pFABP4 and palmitate-bound pFABP5 possess different ligand-binding modes and a unique ligand-binding pocket due to several sequence dissimilarities (A76/L78, T30/M32, underlining indicates pFABP4 residues) between the two proteins. Structural comparison revealed significantly different conformational changes in the β3-β4 loop region (residues 57-62) as well as the flipped Phe60 residue of pFABP5 than that in pFABP4 (the corresponding residue is Phe58). A ligand-binding study using fluorophore displacement assays shows that pFABP4 has a relatively strong affinity for linoleate as compared to pFABP5. In contrast, pFABP5 exhibits higher affinity for palmitate than that for pFABP4. In conclusion, our high-resolution structures and ligand-binding studies provide useful insights into the ligand-binding preferences of pFABPs based on key protein-ligand interactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Polar Life Sciences, Korea Polar Research Institute, Incheon 406-840, Republic of Korea; Department of Polar Sciences, University of Science and Technology, Incheon 406-840, Republic of Korea.