Biochemical and Structural Insights into the Aminotransferase CrmG in Caerulomycin Biosynthesis
Zhu, Y., Xu, J., Mei, X., Feng, Z., Zhang, L., Zhang, Q., Zhang, G., Zhu, W., Liu, J., Zhang, C.(2016) ACS Chem Biol 11: 943-952
- PubMed: 26714051
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.5b00984
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
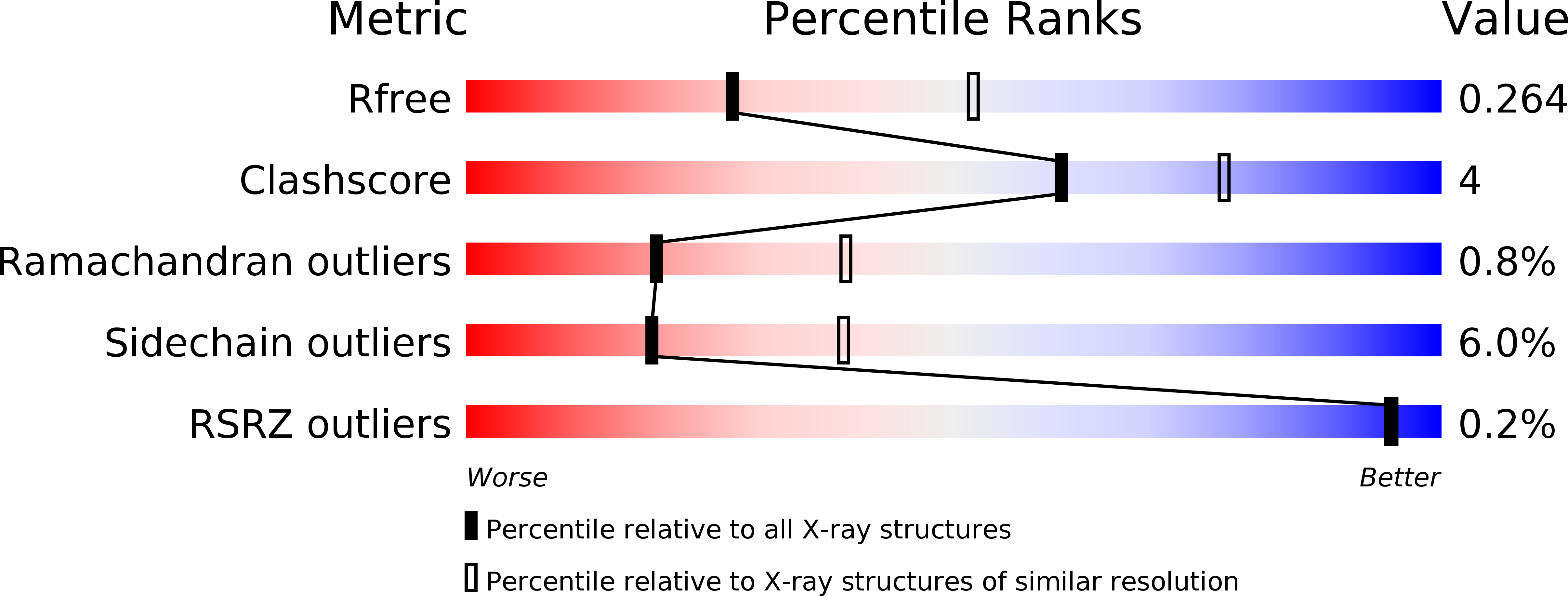
5DDS, 5DDU, 5DDW - PubMed Abstract:
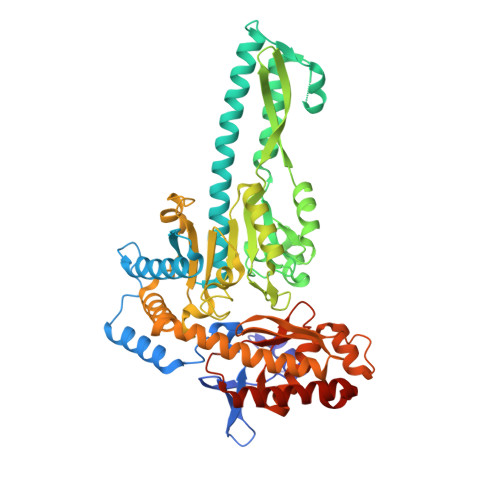
Caerulomycin A (CRM A 1) belongs to a family of natural products containing a 2,2'-bipyridyl ring core structure and is currently under development as a potent novel immunosuppressive agent. Herein, we report the functional characterization, kinetic analysis, substrate specificity, and structure insights of an aminotransferase CrmG in 1 biosynthesis. The aminotransferase CrmG was confirmed to catalyze a key transamination reaction to convert an aldehyde group to an amino group in the 1 biosynthetic pathway, preferring l-glutamate and l-glutamine as the amino donor substrates. The crystal structures of CrmG in complex with the cofactor 5'-pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) or 5'-pyridoxamine phosphate (PMP) or the acceptor substrate were determined to adopt a canonical fold-type I of PLP-dependent enzymes with a unique small additional domain. The structure guided site-directed mutagenesis identified key amino acid residues for substrate binding and catalytic activities, thus providing insights into the transamination mechanism of CrmG.
Organizational Affiliation:
CAS Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica, RNAM Center for Marine Microbiology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences , 164 West Xingang Road, Guangzhou 510301, China.