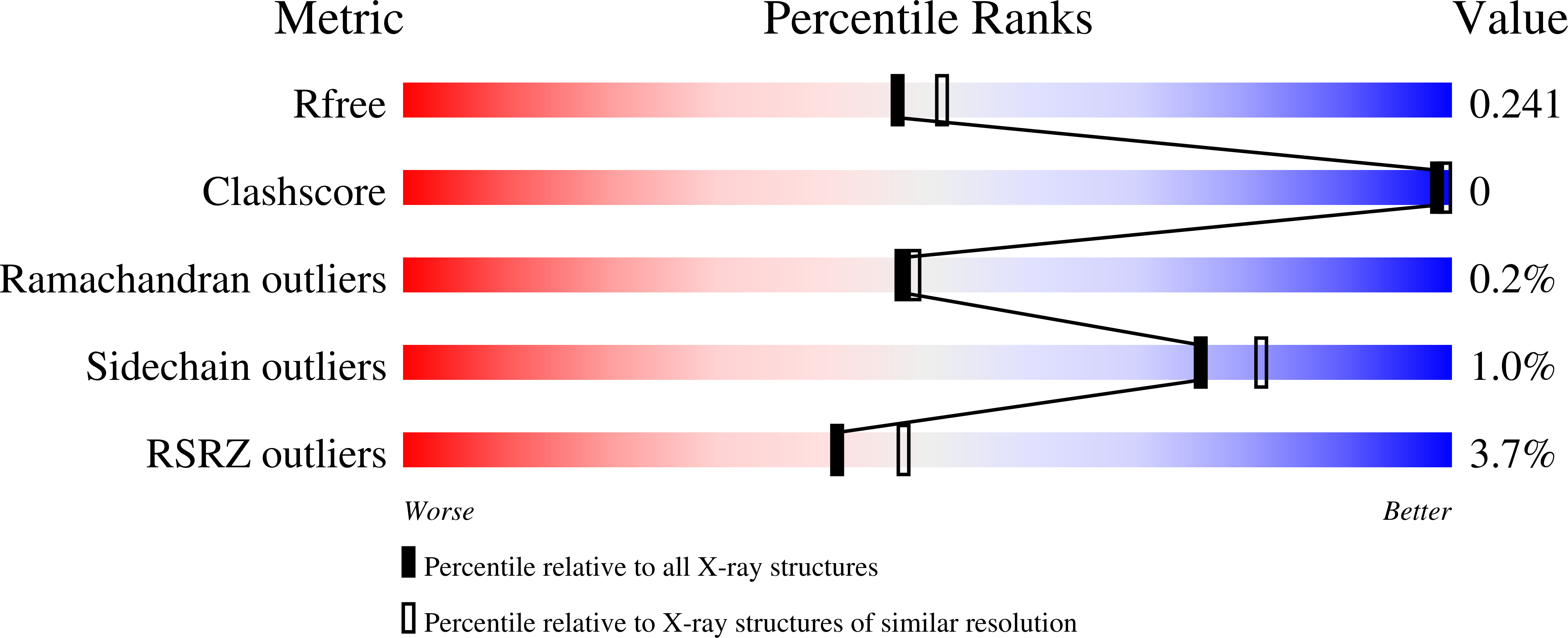
Increase of enzyme activity through specific covalent modification with fragments.
Darby, J.F., Atobe, M., Firth, J.D., Bond, P., Davies, G.J., O'Brien, P., Hubbard, R.E.(2017) Chem Sci 8: 7772-7779
- PubMed: 29163914
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c7sc01966a
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5MI4, 5MI5, 5MI6, 5MI7 - PubMed Abstract:
Modulation of enzyme activity is a powerful means of probing cellular function and can be exploited for diverse applications. Here, we explore a method of enzyme activation where covalent tethering of a small molecule to an enzyme can increase catalytic activity ( k cat / K M ) up to 35-fold. Using a bacterial glycoside hydrolase, BtGH84, we demonstrate how small molecule "fragments", identified as activators in free solution, can be covalently tethered to the protein using Michael-addition chemistry. We show how tethering generates a constitutively-activated enzyme-fragment conjugate, which displays both improved catalytic efficiency and increased susceptibility to certain inhibitor classes. Structure guided modifications of the tethered fragment demonstrate how specific interactions between the fragment and the enzyme influence the extent of activation. This work suggests that a similar approach may be used to modulate the activity of enzymes such as to improve catalytic efficiency or increase inhibitor susceptibility.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry , University of York , Heslington , York , YO10 5DD , UK . Email: [email protected].