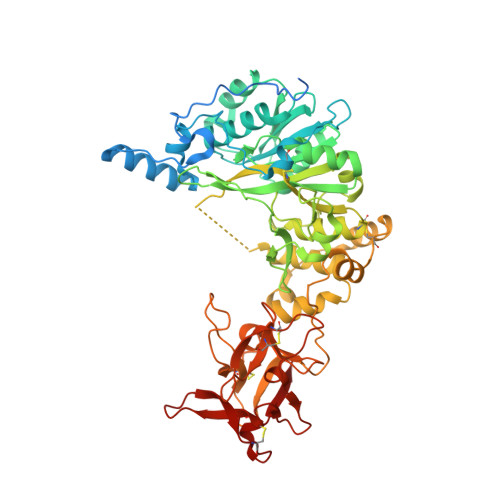
The interdomain flexible linker of the polypeptide GalNAc transferases dictates their long-range glycosylation preferences.
Rivas, M.L., Lira-Navarrete, E., Daniel, E.J.P., Companon, I., Coelho, H., Diniz, A., Jimenez-Barbero, J., Peregrina, J.M., Clausen, H., Corzana, F., Marcelo, F., Jimenez-Oses, G., Gerken, T.A., Hurtado-Guerrero, R.(2017) Nat Commun 8: 1959-1959
- PubMed: 29208955
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02006-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5NQA - PubMed Abstract:
The polypeptide GalNAc-transferases (GalNAc-Ts), that initiate mucin-type O-glycosylation, consist of a catalytic and a lectin domain connected by a flexible linker. In addition to recognizing polypeptide sequence, the GalNAc-Ts exhibit unique long-range N- and/or C-terminal prior glycosylation (GalNAc-O-Ser/Thr) preferences modulated by the lectin domain. Here we report studies on GalNAc-T4 that reveal the origins of its unique N-terminal long-range glycopeptide specificity, which is the opposite of GalNAc-T2. The GalNAc-T4 structure bound to a monoglycopeptide shows that the GalNAc-binding site of its lectin domain is rotated relative to the homologous GalNAc-T2 structure, explaining their different long-range preferences. Kinetics and molecular dynamics simulations on several GalNAc-T2 flexible linker constructs show altered remote prior glycosylation preferences, confirming that the flexible linker dictates the rotation of the lectin domain, thus modulating the GalNAc-Ts' long-range preferences. This work for the first time provides the structural basis for the different remote prior glycosylation preferences of the GalNAc-Ts.
Organizational Affiliation:
BIFI, University of Zaragoza, BIFI-IQFR (CSIC) Joint Unit, Mariano Esquillor s/n, Campus Rio Ebro, Edificio I+D, Zaragoza, 50018, Spain.