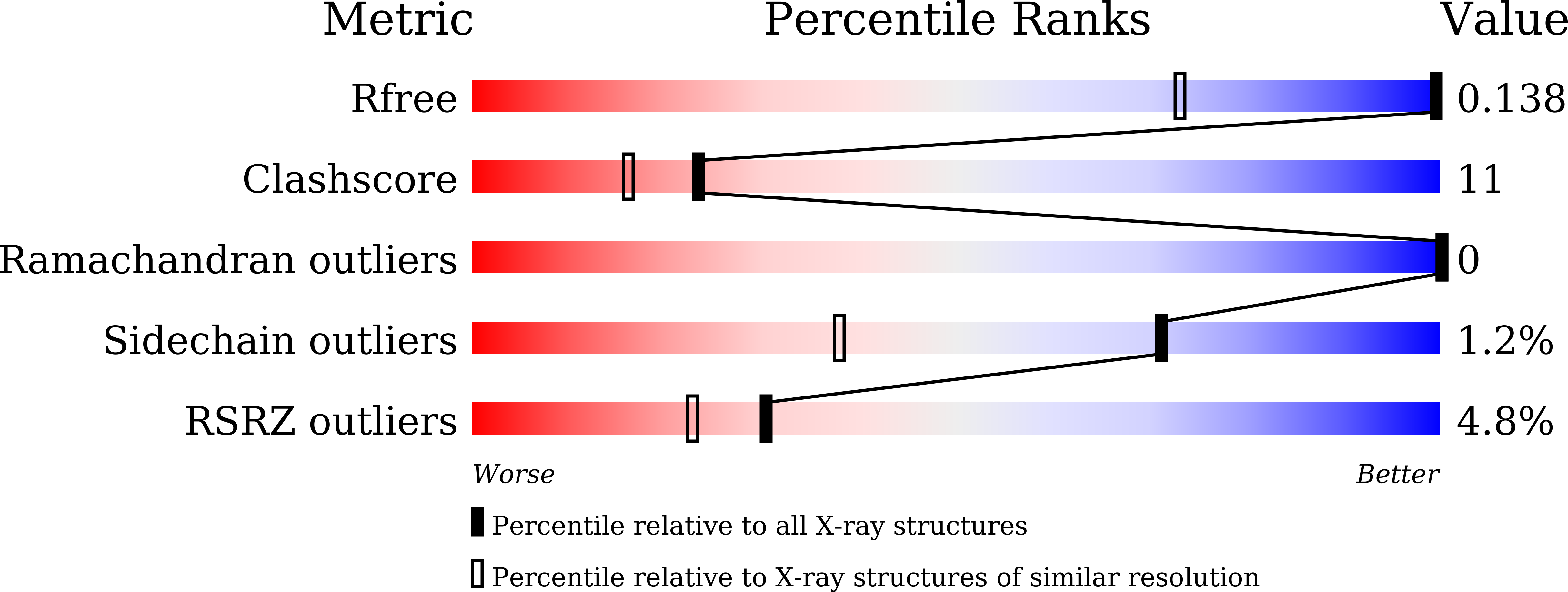
Subatomic structure of hyper-sweet thaumatin D21N mutant reveals the importance of flexible conformations for enhanced sweetness.
Masuda, T., Okubo, K., Murata, K., Mikami, B., Sugahara, M., Suzuki, M., Temussi, P.A., Tani, F.(2019) Biochimie 157: 57-63
- PubMed: 30389513
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2018.10.020
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5X9L, 5X9M - PubMed Abstract:
One of the sweetest proteins found in tropical fruits (with a threshold of 50 nM), thaumatin, is also used commercially as a sweetener. Our previous study successfully produced the sweetest thaumatin mutant (D21N), designated hyper-sweet thaumatin, which decreases the sweetness threshold to 31 nM. To investigate why the D21N mutant is sweeter than wild-type thaumatin, we compared the structure of the D21N mutant solved at a subatomic resolution of 0.93 Å with that of wild-type thaumatin determined at 0.90 Å. Although the overall structure of the D21N mutant resembles that of wild-type thaumatin, our subatomic resolution analysis successfully assigned and discriminated the detailed atomic positions of side-chains at position 21. The relative B-factor value of the side-chain at position 21 in the D21N mutant was higher than that of wild-type thaumatin, hinting at a greater flexibility of side-chain at 21 in the hyper-sweet D21N mutant. Furthermore, alternative conformations of Lys19, which is hydrogen-bonded to Asp21 in wild-type, were found only in the D21N mutant. Subatomic resolution analysis revealed that flexible conformations at the sites adjacent to positions 19 and 21 play a crucial role in enhancing sweet potency and may serve to enhance the complementarity of electrostatic potentials for interaction with the sweet taste receptor.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Food Science and Biotechnology, Graduate School of Agriculture, Kyoto University, Gokasho, Uji, Kyoto, 611-0011, Japan. Electronic address: [email protected].