Molecular basis for the specific recognition of the metazoan cyclic GMP-AMP by the innate immune adaptor protein STING.
Shi, H., Wu, J., Chen, Z.J., Chen, C.(2015) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112: 8947-8952
- PubMed: 26150511
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1507317112
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
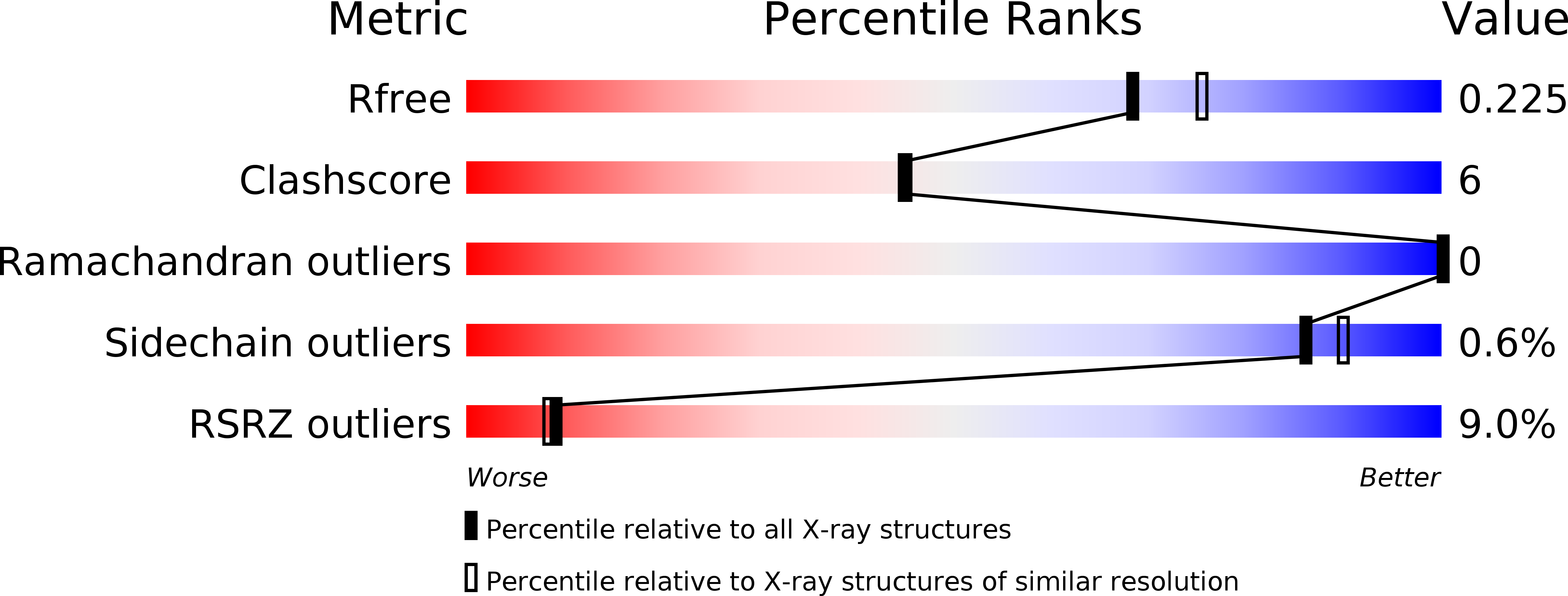
5BQX - PubMed Abstract:
Cyclic GMP-AMP containing a unique combination of mixed phosphodiester linkages (2'3'-cGAMP) is an endogenous second messenger molecule that activates the type-I IFN pathway upon binding to the homodimer of the adaptor protein STING on the surface of endoplasmic reticulum membrane. However, the preferential binding of the asymmetric ligand 2'3'-cGAMP to the symmetric dimer of STING represents a physicochemical enigma. Here we show that 2'3'-cGAMP, but not its linkage isomers, adopts an organized free-ligand conformation that resembles the STING-bound conformation and pays low entropy and enthalpy costs in converting into the active conformation. Our results demonstrate that analyses of free-ligand conformations can be as important as analyses of protein conformations in understanding protein-ligand interactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX 75390;