Dual conformation of the ligand induces the partial agonistic activity of retinoid X receptor alpha (RXR alpha ).
Miyashita, Y., Numoto, N., Arulmozhiraja, S., Nakano, S., Matsuo, N., Shimizu, K., Shibahara, O., Fujihara, M., Kakuta, H., Ito, S., Ikura, T., Ito, N., Tokiwa, H.(2019) FEBS Lett 593: 242-250
- PubMed: 30565665
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13301
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
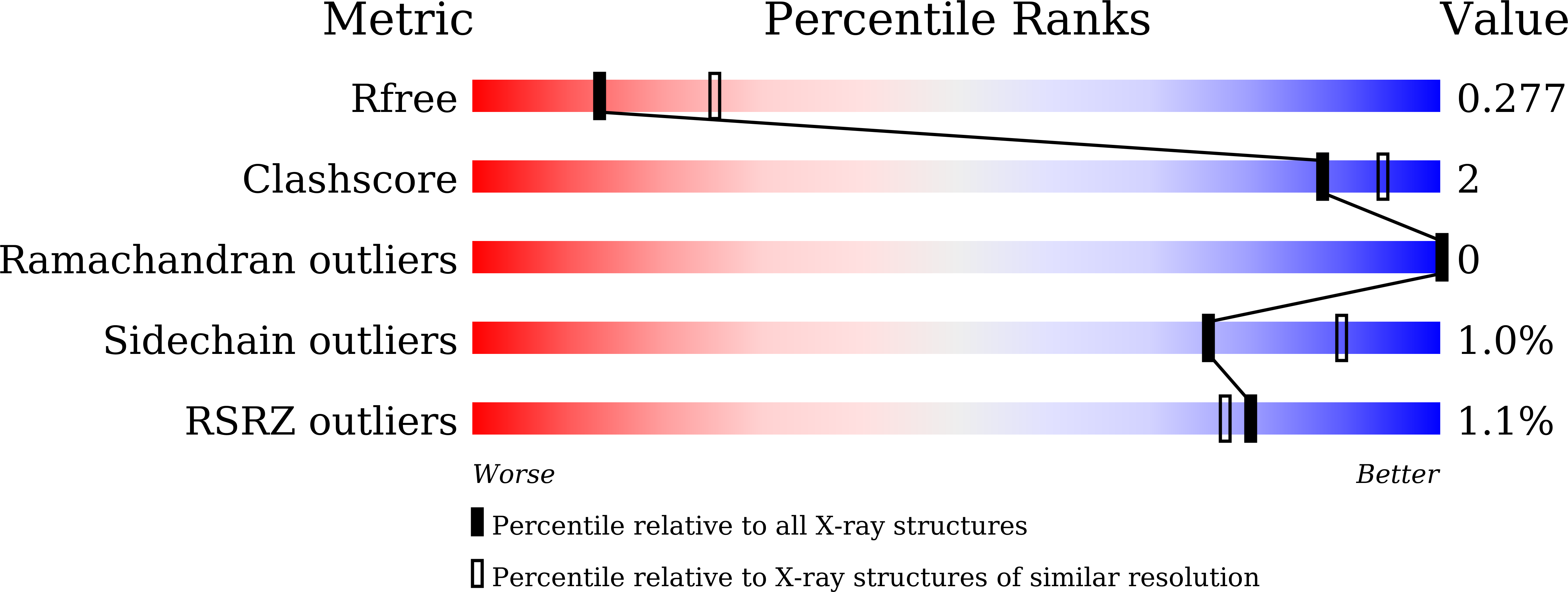
5ZQU - PubMed Abstract:
1-[(3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-yl)amino]benzotriazole-5-carboxylic acid (CBt-PMN), a partial agonist of retinoid X receptor (RXR), has attracted attention due to its potential to treat type 2 diabetes and central nervous system diseases with reduced adverse effects of existing full agonists. Herein, we report the crystal structure of CBt-PMN-bound ligand-binding domain of human RXRα (hRXRα) and its biochemical characterization. Interestingly, the structure is a tetramer in nature, in which CBt-PMNs are clearly found binding in two different conformations. The dynamics of the hRXRα/CBt-PMN complex examined using molecular dynamics simulations suggest that the flexibility of the AF-2 interface depends on the conformation of the ligand. These facts reveal that the dual conformation of CBt-PMN in the complex is probably the reason behind its partial agonistic activity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Rikkyo University, Tokyo, Japan.