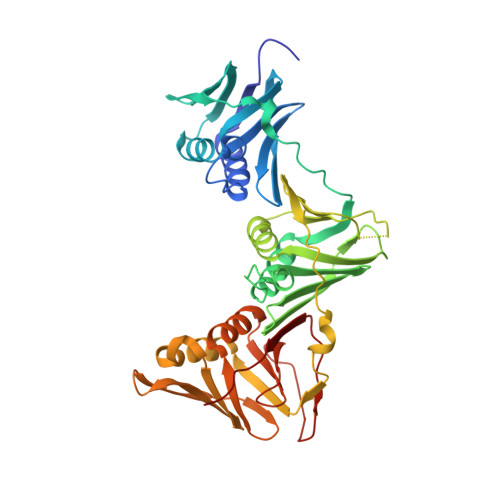
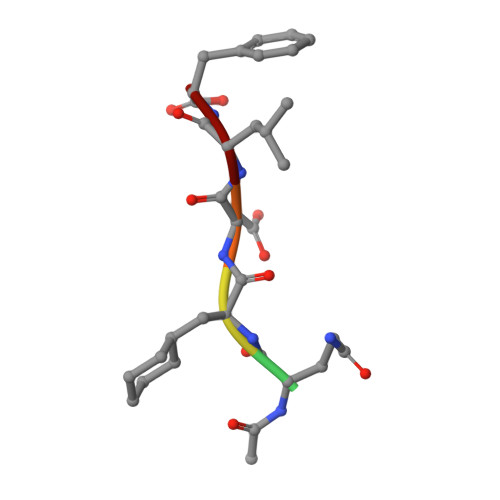
Peptide Interactions on Bacterial Sliding Clamps.
Andre, C., Martiel, I., Wolff, P., Landolfo, M., Lorber, B., Silva da Veiga, C., Dejaegere, A., Dumas, P., Guichard, G., Olieric, V., Wagner, J.G., Burnouf, D.Y.(2019) ACS Infect Dis
- PubMed: 30912430
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsinfecdis.9b00089
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6FVL, 6FVM, 6FVN, 6FVO - PubMed Abstract:
Bacterial sliding clamps control the access of DNA polymerases to the replication fork and are appealing targets for antibacterial drug development. It is therefore essential to decipher the polymerase-clamp binding mode across various bacterial species. Here, two residues of the E. coli clamp binding pocket, Ec S 346 and Ec M 362 , and their cognate residues in M. tuberculosis and B. subtilis clamps, were mutated. The effects of these mutations on the interaction of a model peptide with these variant clamps were evaluated by thermodynamic, molecular dynamics, X-rays crystallography, and biochemical analyses. Ec M 362 and corresponding residues in Gram positive clamps occupy a strategic position where a mobile residue is essential for an efficient peptide interaction. Ec S 346 has a more subtle function that modulates the pocket folding dynamics, while the equivalent residue in B. subtilis is essential for polymerase activity and might therefore be a Gram positive-specific molecular marker. Finally, the peptide binds through an induced-fit process to Gram negative and positive pockets, but the complex stability varies according to a pocket-specific network of interactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut Européen de Chimie et Biologie , Université de Bordeaux-CNRS UMR 5248, CBMN , 2, rue Robert Escarpit , 33607 Pessac , France.