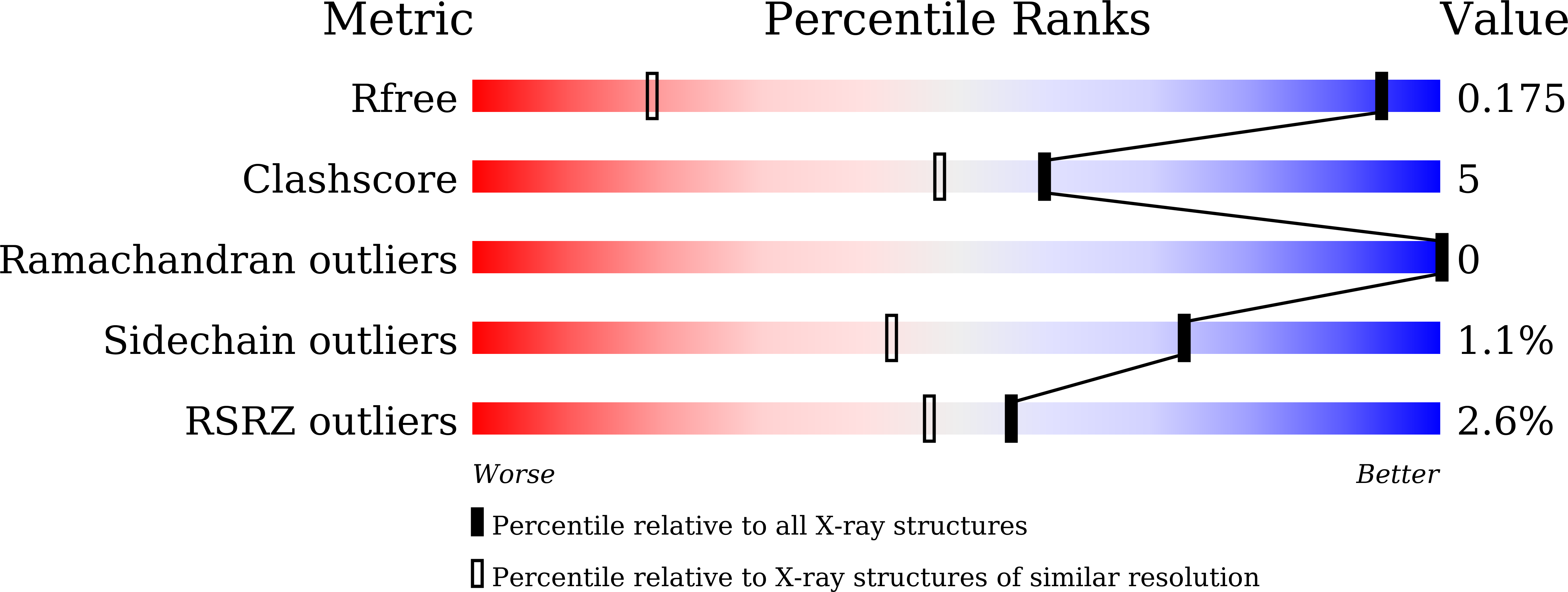
Second messenger Ap4A polymerizes target protein HINT1 to transduce signals in Fc epsilon RI-activated mast cells.
Yu, J., Liu, Z., Liang, Y., Luo, F., Zhang, J., Tian, C., Motzik, A., Zheng, M., Kang, J., Zhong, G., Liu, C., Fang, P., Guo, M., Razin, E., Wang, J.(2019) Nat Commun 10: 4664-4664
- PubMed: 31604935
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12710-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5ED3, 5ED6, 6J53, 6J58, 6J5S, 6J5Z, 6J64, 6J65 - PubMed Abstract:
Signal transduction systems enable organisms to monitor their external environments and accordingly adjust the cellular processes. In mast cells, the second messenger Ap 4 A binds to the histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1 (HINT1), disrupts its interaction with the microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF), and eventually activates the transcription of genes downstream of MITF in response to immunostimulation. How the HINT1 protein recognizes and is regulated by Ap 4 A remain unclear. Here, using eight crystal structures, biochemical experiments, negative stain electron microscopy, and cellular experiments, we report that Ap 4 A specifically polymerizes HINT1 in solution and in activated rat basophilic leukemia cells. The polymerization interface overlaps with the area on HINT1 for MITF interaction, suggesting a possible competitive mechanism to release MITF for transcriptional activation. The mechanism depends precisely on the length of the phosphodiester linkage of Ap 4 A. These results highlight a direct polymerization signaling mechanism by the second messenger.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Bioorganic and Natural Products Chemistry, Center for Excellence in Molecular Synthesis, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 345 Lingling Road, Shanghai, 200032, China.