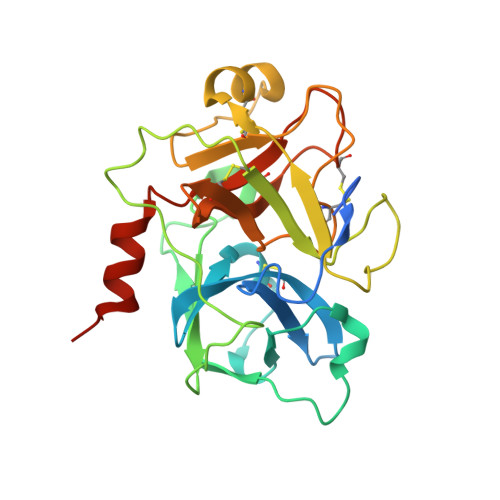
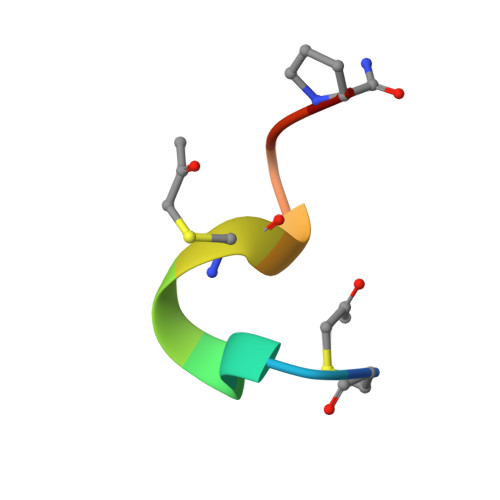
De novo development of proteolytically resistant therapeutic peptides for oral administration.
Kong, X.D., Moriya, J., Carle, V., Pojer, F., Abriata, L.A., Deyle, K., Heinis, C.(2020) Nat Biomed Eng 4: 560-571
- PubMed: 32393891
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-020-0556-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6TWB, 6TWC - PubMed Abstract:
The oral administration of peptide drugs is hampered by their metabolic instability and limited intestinal uptake. Here, we describe a method for the generation of small target-specific peptides (less than 1,600 Da in size) that resist gastrointestinal proteases. By using phage display to screen large libraries of genetically encoded double-bridged peptides on protease-resistant fd bacteriophages, we generated a peptide inhibitor of the coagulation Factor XIa with nanomolar affinity that resisted gastrointestinal proteases in all regions of the gastrointestinal tract of mice after oral administration, enabling more than 30% of the peptide to remain intact, and small quantities of it to reach the blood circulation. We also developed a gastrointestinal-protease-resistant peptide antagonist for the interleukin-23 receptor, which has a role in the pathogenesis of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. The de novo generation of targeted peptides that resist proteolytic degradation in the gastrointestinal tract should help the development of effective peptides for oral delivery.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Chemical Sciences and Engineering, School of Basic Sciences, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland.