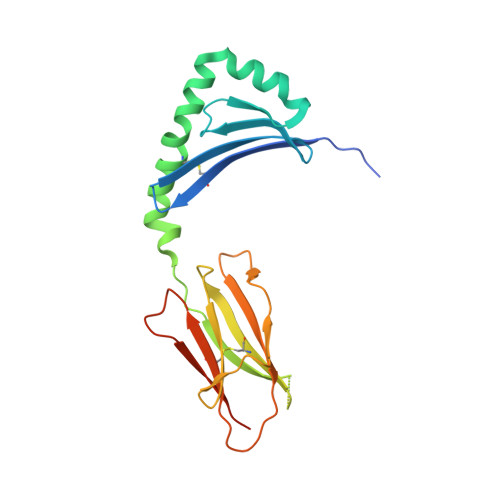
T cell receptor cross-reactivity between gliadin and bacterial peptides in celiac disease.
Petersen, J., Ciacchi, L., Tran, M.T., Loh, K.L., Kooy-Winkelaar, Y., Croft, N.P., Hardy, M.Y., Chen, Z., McCluskey, J., Anderson, R.P., Purcell, A.W., Tye-Din, J.A., Koning, F., Reid, H.H., Rossjohn, J.(2020) Nat Struct Mol Biol 27: 49-61
- PubMed: 31873306
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-019-0353-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
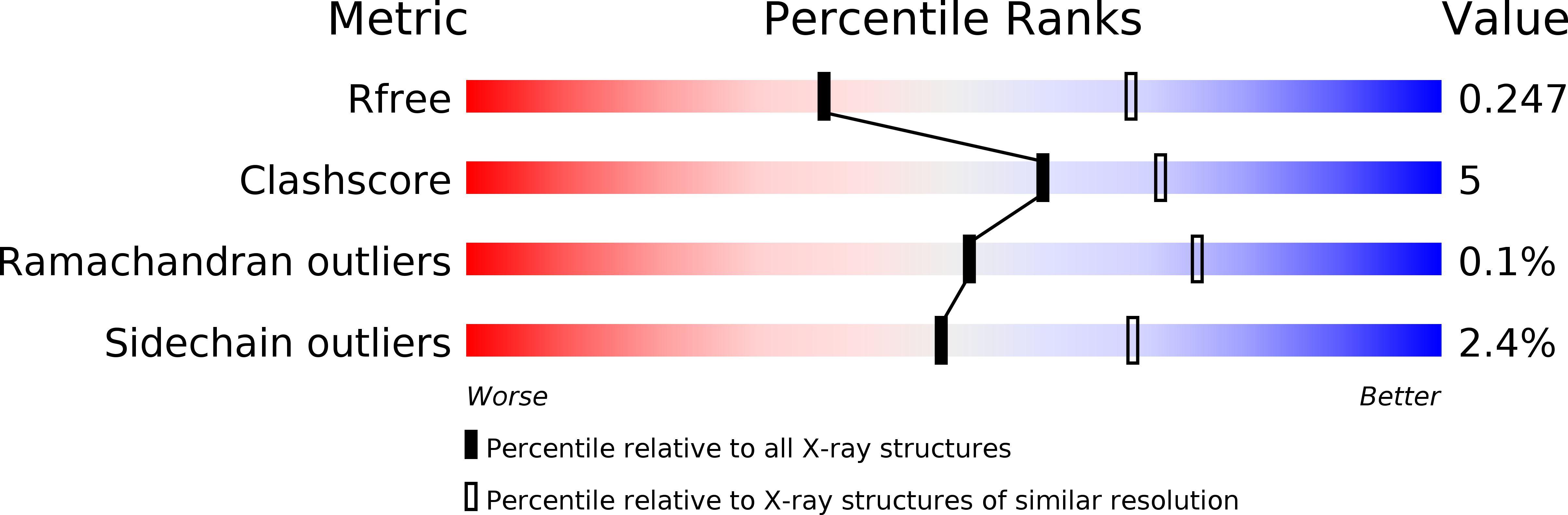
6U3M, 6U3N, 6U3O - PubMed Abstract:
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) locus is strongly associated with T cell-mediated autoimmune disorders. HLA-DQ2.5-mediated celiac disease (CeD) is triggered by the ingestion of gluten, although the relative roles of genetic and environmental risk factors in CeD is unclear. Here we identify microbially derived mimics of gliadin epitopes and a parental bacterial protein that is naturally processed by antigen-presenting cells and activated gliadin reactive HLA-DQ2.5-restricted T cells derived from CeD patients. Crystal structures of T cell receptors in complex with HLA-DQ2.5 bound to two distinct bacterial peptides demonstrate that molecular mimicry underpins cross-reactivity toward the gliadin epitopes. Accordingly, gliadin reactive T cells involved in CeD pathogenesis cross-react with ubiquitous bacterial peptides, thereby suggesting microbial exposure as a potential environmental factor in CeD.
Organizational Affiliation:
Infection and Immunity Program and The Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Biomedicine Discovery Institute Monash University, Clayton, Victoria, Australia.