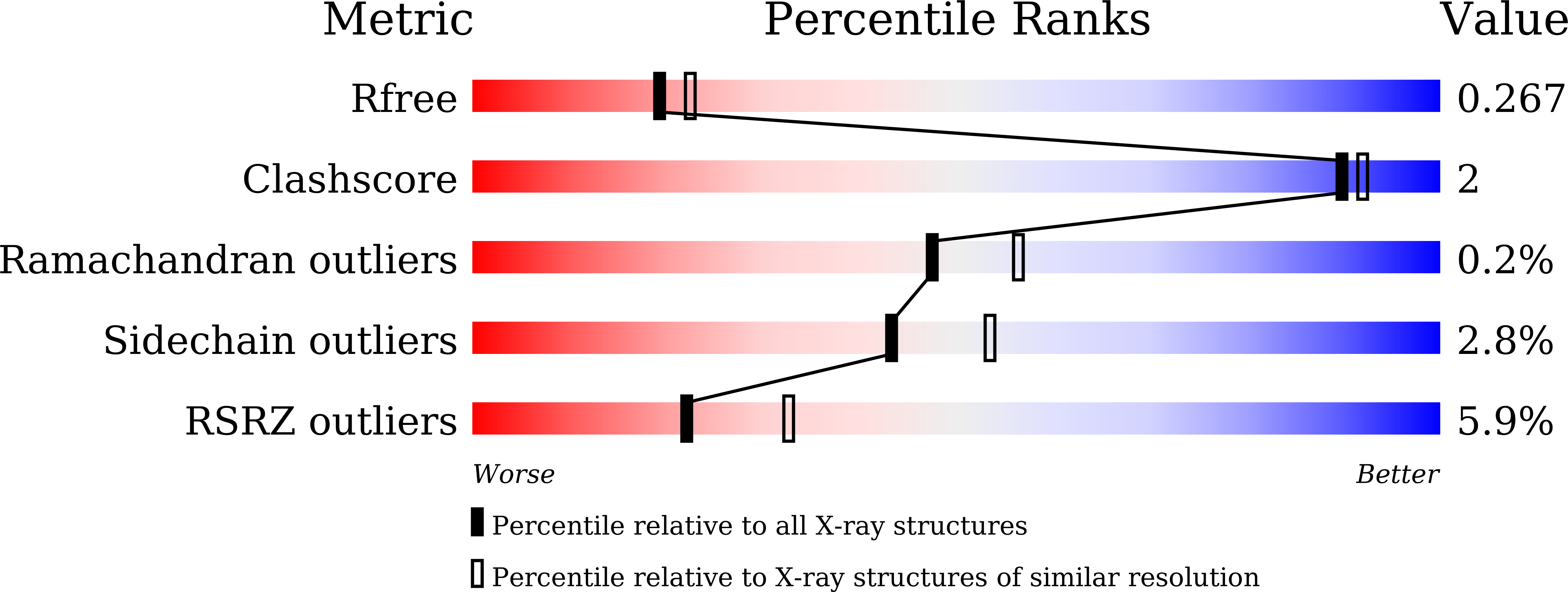
Tumors exploit FTO-mediated regulation of glycolytic metabolism to evade immune surveillance.
Liu, Y., Liang, G., Xu, H., Dong, W., Dong, Z., Qiu, Z., Zhang, Z., Li, F., Huang, Y., Li, Y., Wu, J., Yin, S., Zhang, Y., Guo, P., Liu, J., Xi, J.J., Jiang, P., Han, D., Yang, C.G., Xu, M.M.(2021) Cell Metab 33: 1221-1233.e11
- PubMed: 33910046
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2021.04.001
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7CKK - PubMed Abstract:
The ever-increasing understanding of the complexity of factors and regulatory layers that contribute to immune evasion facilitates the development of immunotherapies. However, the diversity of malignant tumors limits many known mechanisms in specific genetic and epigenetic contexts, manifesting the need to discover general driver genes. Here, we have identified the m 6 A demethylase FTO as an essential epitranscriptomic regulator utilized by tumors to escape immune surveillance through regulation of glycolytic metabolism. We show that FTO-mediated m 6 A demethylation in tumor cells elevates the transcription factors c-Jun, JunB, and C/EBPβ, which allows the rewiring of glycolytic metabolism. Fto knockdown impairs the glycolytic activity of tumor cells, which restores the function of CD8 + T cells, thereby inhibiting tumor growth. Furthermore, we developed a small-molecule compound, Dac51, that can inhibit the activity of FTO, block FTO-mediated immune evasion, and synergize with checkpoint blockade for better tumor control, suggesting reprogramming RNA epitranscriptome as a potential strategy for immunotherapy.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Basic Medical Sciences, School of Medicine, Institute for Immunology, Beijing Key Lab for Immunological Research on Chronic Diseases, THU-PKU Center for Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China.