Molecular Insights into the Assembly and Functional Diversification of Typhoid Toxin.
Liu, X., Chen, Z., Jiao, X., Jiang, X., Qiu, J., You, F., Long, H., Cao, H., Fowler, C.C., Gao, X.(2022) mBio 13
- PubMed: 35012347
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.01916-21
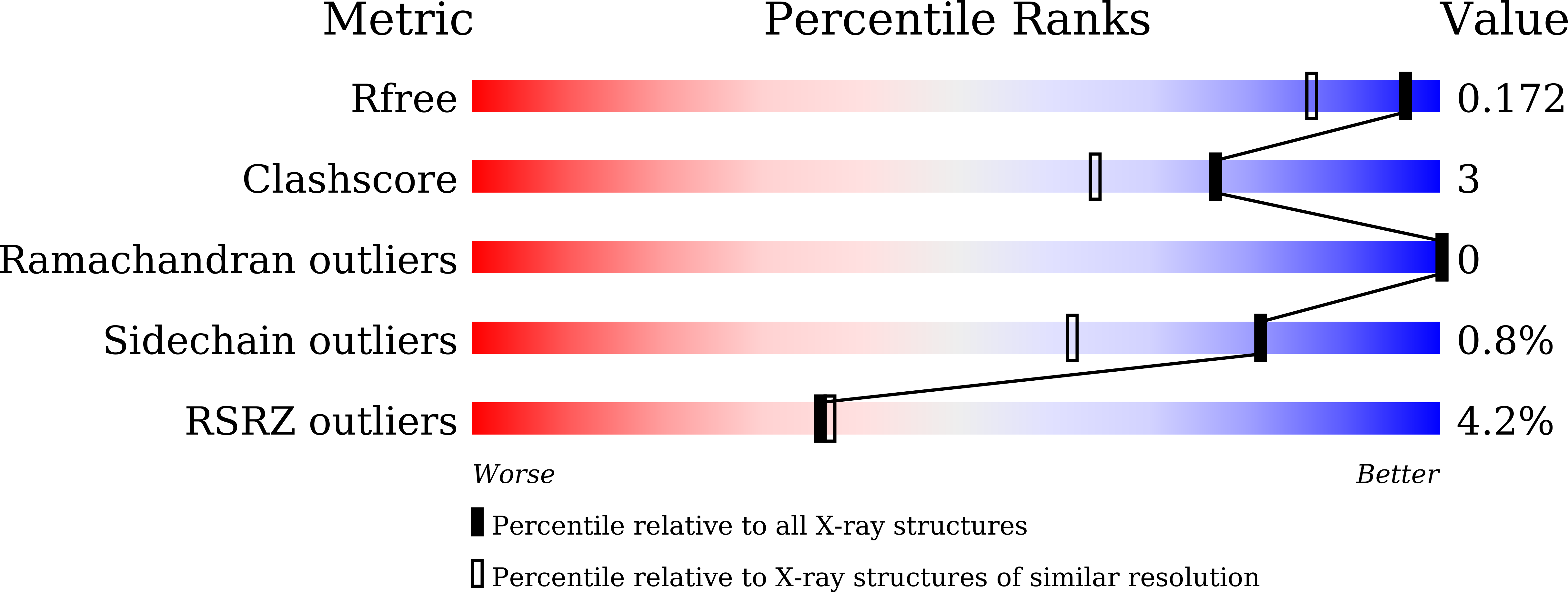
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7EE3, 7EE4, 7EE5, 7EE6 - PubMed Abstract:
Typhoid toxin is an A 2 B 5 protein toxin and an important virulence factor for the human-adapted bacterial pathogen Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi, the causative agent of typhoid fever. Typhoid toxin contains two enzymatic subunits, PltA and CdtB, which dock onto a pentameric delivery platform composed of the protein PltB. It was recently reported that the same enzymatic subunits can assemble with a different delivery platform composed of the protein PltC, forming a distinct version of typhoid toxin. However, the differences in structure and receptor specificity between the PltC and PltB typhoid toxins remain unknown. Here, we determined atomic-level structures of the pentameric PltC subunit, the fully assembled PltC typhoid toxin, and the PltC pentamers in complex with glycan receptors. Biochemical and structural analyses indicate that PltB and PltC are unable to form heteromeric delivery complexes due to electrostatic repulsion at the subunit interface and thus form separate toxins only. We further observed that, despite low sequence similarity between PltB and PltC, they interact with PltA in a similar manner but that PltC exhibits stronger electrostatic interactions with PltA, enabling it to outcompete PltB in toxin assembly. The ligand-bound atomic structures of PltC show an additional glycan binding site not found in PltB and glycan array analysis indicates that PltB and PltC exhibit significant differences in glycan binding specificity. Collectively, this study offers atomic-level insights into how S . Typhi produces two distinct versions of typhoid toxin, thereby generating functional diversity in this key virulence factor. IMPORTANCE Typhoid fever is a devastating disease that kills more than 115,000 people every year and is caused by Salmonella Typhi. Typhoid toxin, exclusively produced by S . Typhi, was demonstrated to be responsible for the pathogenesis of typhoid fever. Typhoid toxin consists of a pentameric delivery B subunit to transport the catalytic A subunits into the host cell through binding of the glycan receptors. Recent study shows that S . Typhi encodes two homologous delivery B subunits that are able to associate with the same active subunits to produce alternative toxins with distinct functional characteristics. Here, we show that the two delivery subunits can form only homopentameric delivery platforms that compete to associate with typhoid toxin's active subunits and that the two resulting toxins have distinct glycan-binding properties that confer distinct functional traits. These findings highlight the unique assembly and functional diversification of typhoid toxins.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Microbial Technology, Shandong Universitygrid.27255.37, Qingdao, China.