Design, Synthesis and X-Ray Structural Studies of Potent HIV-1 Protease Inhibitors Containing C-4 Substituted Tricyclic Hexahydro-Furofuran Derivatives as P2 Ligands.
Ghosh, A.K., Kovela, S., Sharma, A., Shahabi, D., Ghosh, A.K., Hopkins, D.R., Yadav, M., Johnson, M.E., Agniswamy, J., Wang, Y.F., Hattori, S.I., Higashi-Kuwata, N., Aoki, M., Amano, M., Weber, I.T., Mitsuya, H.(2022) ChemMedChem 17: e202200058-e202200058
- PubMed: 35170223
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.202200058
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
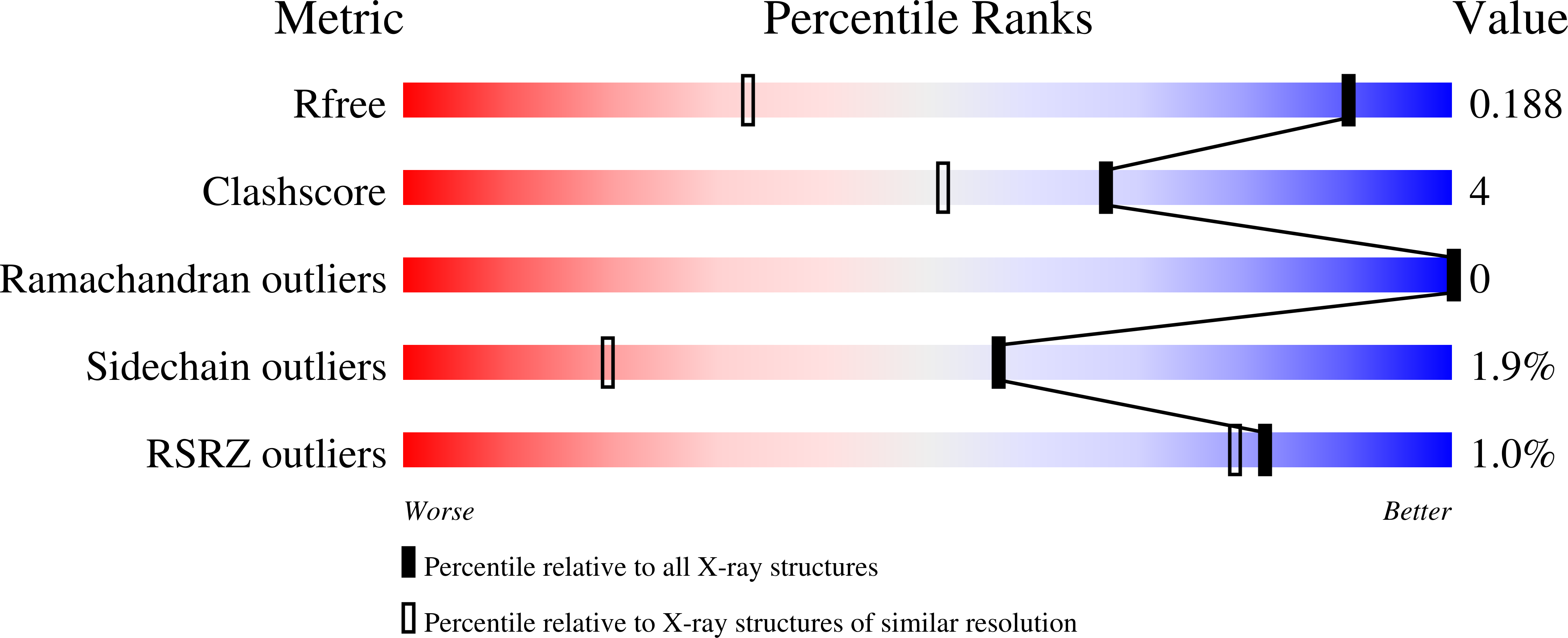
7TO5, 7TO6 - PubMed Abstract:
The design, synthesis, X-ray structural, and biological evaluation of a series of highly potent HIV-1 protease inhibitors are reported herein. These inhibitors incorporate novel cyclohexane-fused tricyclic bis-tetrahydrofuran as P2 ligands in combination with a variety of P1 and P2' ligands. The inhibitor with a difluoromethylphenyl P1 ligand and a cyclopropylaminobenzothiazole P2' ligand exhibited the most potent antiviral activity. Also, it maintained potent antiviral activity against a panel of highly multidrug-resistant HIV-1 variants. The corresponding inhibitor with an enantiomeric ligand was significantly less potent in these antiviral assays. The new P2 ligands were synthesized in optically active form using enzymatic desymmetrization of meso-diols as the key step. To obtain molecular insight, two high-resolution X-ray structures of inhibitor-bound HIV-1 protease were determined and structural analyses have been highlighted.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Department of Medicinal Chemistry, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47907, USA.