Inhibition of Fosfomycin Resistance Protein FosB from Gram-Positive Pathogens by Phosphonoformate.
Travis, S., Green, K.D., Gilbert, N.C., Tsodikov, O.V., Garneau-Tsodikova, S., Thompson, M.K.(2023) Biochemistry 62: 109-117
- PubMed: 36525630
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.2c00566
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
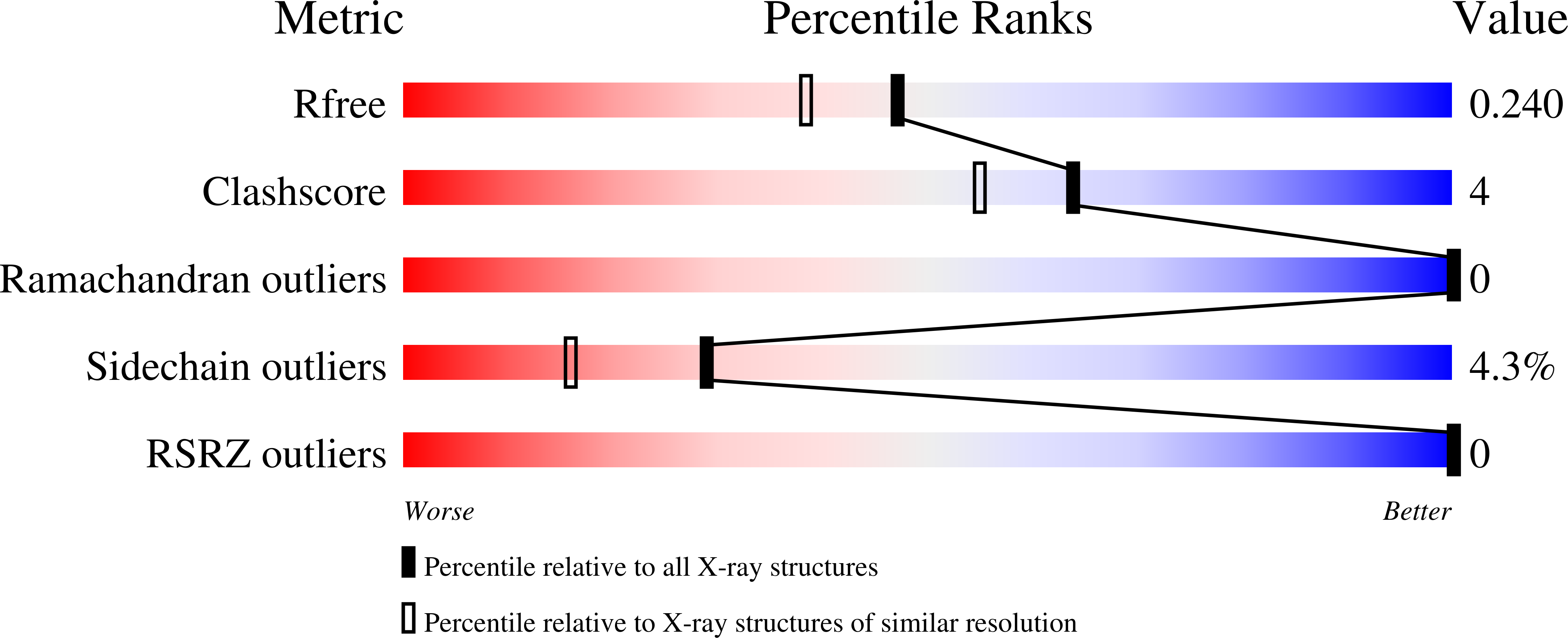
8DTD - PubMed Abstract:
The Gram-positive pathogen Staphylococcus aureus is a leading cause of antimicrobial resistance related deaths worldwide. Like many pathogens with multidrug-resistant strains, S. aureus contains enzymes that confer resistance through antibiotic modification(s). One such enzyme present in S. aureus is FosB, a Mn 2+ -dependent l-cysteine or bacillithiol (BSH) transferase that inactivates the antibiotic fosfomycin. fosB gene knockout experiments show that the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of fosfomycin is significantly reduced when the FosB enzyme is not present. This suggests that inhibition of FosB could be an effective method to restore fosfomycin activity. We used high-throughput in silico -based screening to identify small-molecule analogues of fosfomycin that inhibited thiol transferase activity. Phosphonoformate (PPF) was a top hit from our approach. Herein, we have characterized PPF as a competitive inhibitor of FosB from S. aureus (FosB Sa ) and Bacillus cereus (FosB Bc ). In addition, we have determined a crystal structure of FosB Bc with PPF bound in the active site. Our results will be useful for future structure-based development of FosB inhibitors that can be delivered in combination with fosfomycin in order to increase the efficacy of this antibiotic.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry & Biochemistry, The University of Alabama, 250 Hackberry Lane, Tuscaloosa, Alabama 35487, United States.