Developing a structure-function model for the cryptophyte phycoerythrin 545 using ultrahigh resolution crystallography and ultrafast laser spectroscopy
Doust, A.B., Marai, C.N.J., Harrop, S.J., Wilk, K.E., Curmi, P.M.G., Scholes, G.D.(2004) J Mol Biol 344: 135-153
- PubMed: 15504407
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.09.044
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1XF6, 1XG0 - PubMed Abstract:
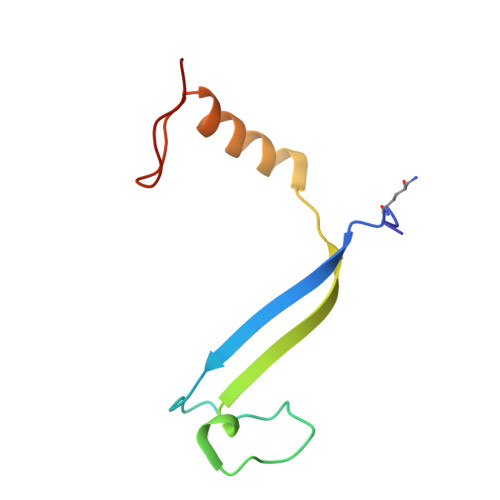
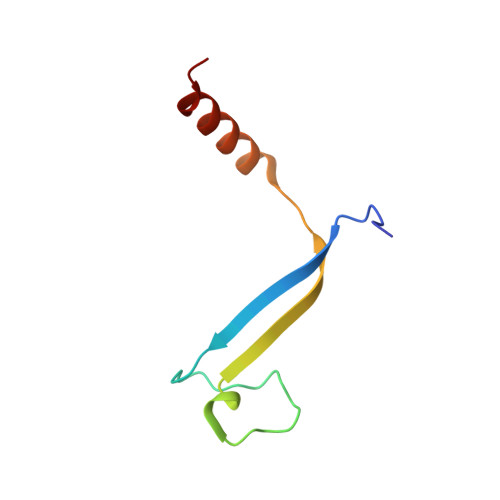
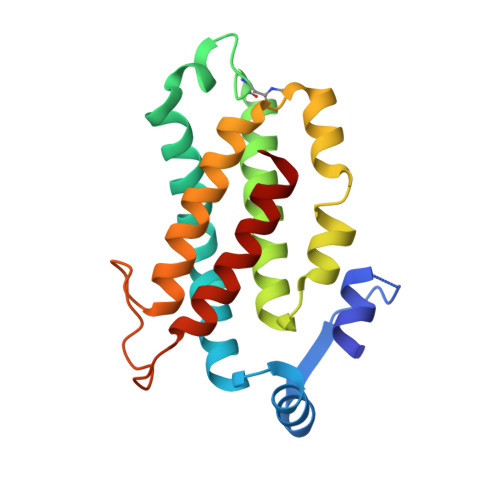
Cryptophyte algae differ from cyanobacteria and red algae in the architecture of their photosynthetic light harvesting systems, even though all three are evolutionarily related. Central to cryptophyte light harvesting is the soluble antenna protein phycoerythrin 545 (PE545). The ultrahigh resolution crystal structure of PE545, isolated from a unicellular cryptophyte Rhodomonas CS24, is reported at both 1.1A and 0.97A resolution, revealing details of the conformation and environments of the chromophores. Absorption, emission and polarized steady state spectroscopy (298K, 77K), as well as ultrafast (20fs time resolution) measurements of population dynamics are reported. Coupled with complementary quantum chemical calculations of electronic transitions of the bilins, these enable assignment of spectral absorption characteristics to each chromophore in the structure. Spectral differences between the tetrapyrrole pigments due to chemical differences between bilins, as well as their binding and interaction with the local protein environment are described. Based on these assignments, and considering customized optical properties such as strong coupling, a model for light harvesting by PE545 is developed which explains the fast, directional harvesting of excitation energy. The excitation energy is funnelled from four peripheral pigments (beta158,beta82) into a central chromophore dimer (beta50/beta61) in approximately 1ps. Those chromophores, in turn, transfer the excitation energy to the red absorbing molecules located at the periphery of the complex in approximately 4ps. A final resonance energy transfer step sensitizes just one of the alpha19 bilins on a time scale of 22ps. Furthermore, it is concluded that binding of PE545 to the thylakoid membrane is not essential for efficient energy transfer to the integral membrane chlorophyll a-containing complexes associated with PS-II.
Organizational Affiliation:
Lash-Miller Chemical Laboratories, University of Toronto, 80 St George Street, Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5S 3H6.