Structural basis for inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor by cetuximab
Li, S., Schmitz, K.R., Jeffrey, P.D., Wiltzius, J.J.W., Kussie, P., Ferguson, K.M.(2005) Cancer Cell 7: 301-311
- PubMed: 15837620
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2005.03.003
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1YY8, 1YY9 - PubMed Abstract:
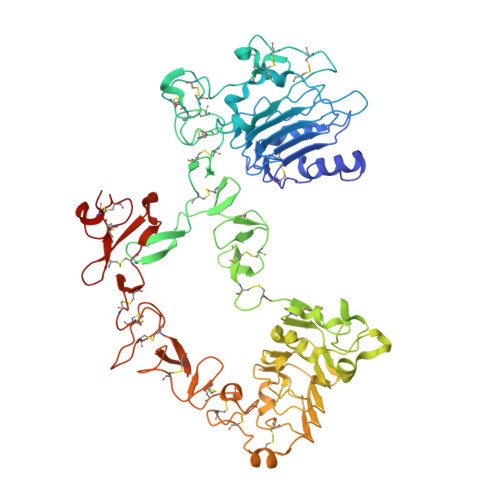
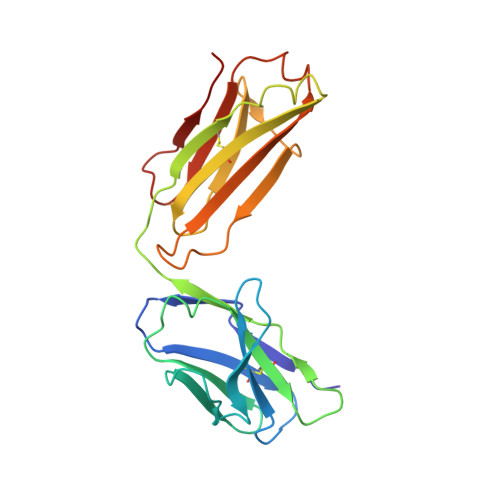
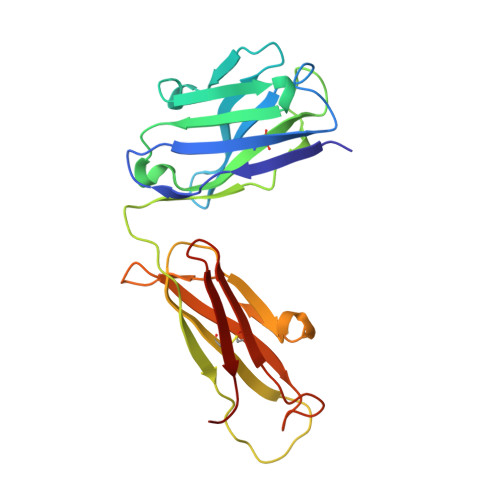
Recent structural studies of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family extracellular regions have identified an unexpected mechanism for ligand-induced receptor dimerization that has important implications for activation and inhibition of these receptors. Here we describe the 2.8 angstroms resolution X-ray crystal structure of the antigen binding (Fab) fragment from cetuximab (Erbitux), an inhibitory anti-EGFR antibody, in complex with the soluble extracellular region of EGFR (sEGFR). The sEGFR is in the characteristic "autoinhibited" or "tethered" inactive configuration. Cetuximab interacts exclusively with domain III of sEGFR, partially occluding the ligand binding region on this domain and sterically preventing the receptor from adopting the extended conformation required for dimerization. We suggest that both these effects contribute to potent inhibition of EGFR activation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Physiology, University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19104, USA.