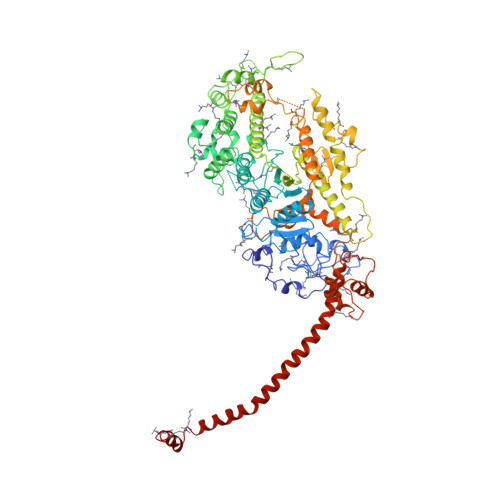
Three-dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1: a molecular motor.
Rayment, I., Rypniewski, W.R., Schmidt-Base, K., Smith, R., Tomchick, D.R., Benning, M.M., Winkelmann, D.A., Wesenberg, G., Holden, H.M.(1993) Science 261: 50-58
- PubMed: 8316857
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.8316857
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2MYS - PubMed Abstract:
Directed movement is a characteristic of many living organisms and occurs as a result of the transformation of chemical energy into mechanical energy. Myosin is one of three families of molecular motors that are responsible for cellular motility. The three-dimensional structure of the head portion of myosin, or subfragment-1, which contains both the actin and nucleotide binding sites, is described. This structure of a molecular motor was determined by single crystal x-ray diffraction. The data provide a structural framework for understanding the molecular basis of motility.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Wisconsin, Madison 53705.