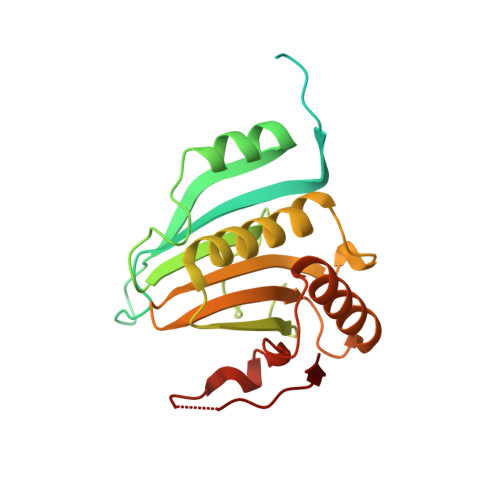
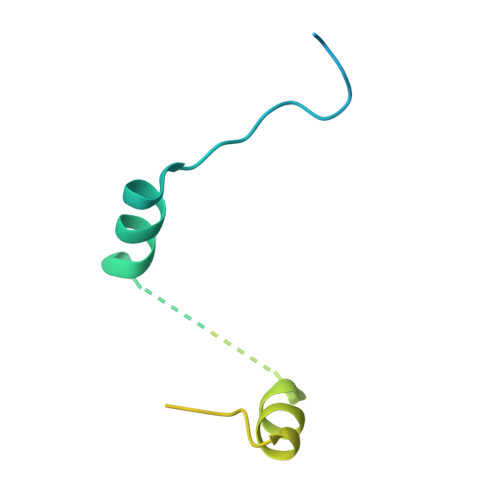
Crystal Structure of a Minimal Eif4E-Cup Complex Revelas a General Mechanism of Eif4E Regulation in Translational Repression
Kinkelin, K., Veith, K., Gruenwald, M., Bono, F.(2012) RNA 18: 1624
- PubMed: 22832024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.033639.112
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4AXG - PubMed Abstract:
Cup is an eIF4E-binding protein (4E-BP) that plays a central role in translational regulation of localized mRNAs during early Drosophila development. In particular, Cup is required for repressing translation of the maternally contributed oskar, nanos, and gurken mRNAs, all of which are essential for embryonic body axis determination. Here, we present the 2.8 Å resolution crystal structure of a minimal eIF4E-Cup assembly, consisting of the interacting regions of the two proteins. In the structure, two separate segments of Cup contact two orthogonal faces of eIF4E. The eIF4E-binding consensus motif of Cup (YXXXXLΦ) binds the convex side of eIF4E similarly to the consensus of other eIF4E-binding proteins, such as 4E-BPs and eIF4G. The second, noncanonical, eIF4E-binding site of Cup binds laterally and perpendicularly to the eIF4E β-sheet. Mutations of Cup at this binding site were shown to reduce binding to eIF4E and to promote the destabilization of the associated mRNA. Comparison with the binding mode of eIF4G to eIF4E suggests that Cup and eIF4G binding would be mutually exclusive at both binding sites. This shows how a common molecular surface of eIF4E might recognize different proteins acting at different times in the same pathway. The structure provides insight into the mechanism by which Cup disrupts eIF4E-eIF4G interaction and has broader implications for understanding the role of 4E-BPs in translational regulation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max-Planck-Institute for Developmental Biology, 71076 Tübingen, Germany.